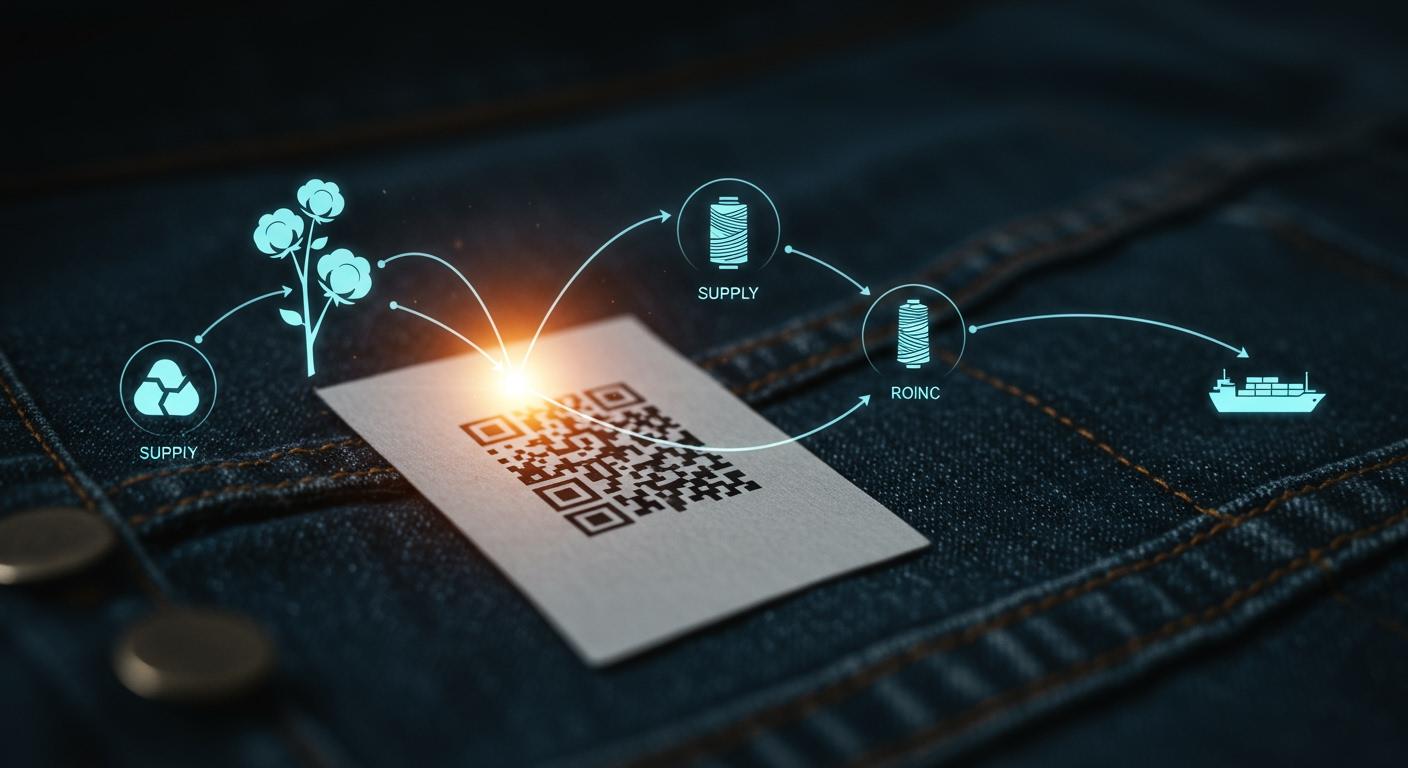

By 2025, the powerful combination of blockchain and AI will create immutable digital passports for fashion items, making the supply chain transparent. This technology allows consumers and brands to verify a product's entire journey, achieving end-to-end transparency and building radical trust. This shift is not a future concept; it is a tangible reality reshaping the industry toward accountability. The future of the supply chain depends on blockchain and AI.
Consumer demand for accountability is clear. 70% of shoppers will pay more for transparent goods, showing a deep need for trust. This era of traceable sourcing, powered by blockchain and AI, directly addresses this need for trust.
The Role of Blockchain in the Supply Chain

Blockchain technology serves as the foundational layer for trust in the modern supply chain. Its core function is to provide an unchangeable, decentralized ledger. This ledger records every transaction, from farm to factory, creating a permanent and shared record. This system enhances supply chain management by improving visibility and reducing information gaps. The use of blockchain technology ultimately lowers administrative costs significantly.
Creating a Single Source of Truth
Blockchain establishes a single, verifiable source of truth for every product. This powerful blockchain technology creates a secure and transparent environment for tracking items. The decentralized nature of blockchain ensures that no single entity controls the data, which is crucial for the complex fashion supply chain. This approach provides unprecedented supply chain transparency and traceability.
- Each transaction is encrypted and linked to the previous one, forming a secure chain.
- Once data is added to the blockchain, it cannot be altered, guaranteeing authenticity.
- Any attempt to falsify product origin is immediately visible to all network participants.
- This inherent security provides complete visibility for senders and receivers.
Many brands already use blockchain solutions for supply chain traceability. These blockchain solutions prove the power of this technology.
| Company/Platform | Blockchain Application for Single Source of Truth |
|---|---|
| VeChain (with H&M) | Uses blockchain for tracking products from raw materials to shelf, ensuring authenticity. |
| Arianee | Provides digital certificates on the blockchain, offering immutable proof of ownership. |
| Ecoalf | Leverages blockchain for tracking recycled materials, giving consumers transparent insights. |
Automating Compliance with Smart Contracts
Smart contracts are self-executing agreements built on blockchain technology. They automatically enforce terms when predefined conditions are met. This automation is a game-changer for supply chain management. Smart contracts eliminate the need for many intermediaries, which makes global trade faster and cheaper. This application of blockchain technology streamlines complex processes.
For cross-border payments, smart contracts drastically reduce settlement times and fees. Traditional methods can take days and incur high costs, but blockchain technology enables near-instant, low-cost transactions. This efficiency in supply chain management is transformative. The blockchain offers better tracking and visibility. The blockchain technology is key.
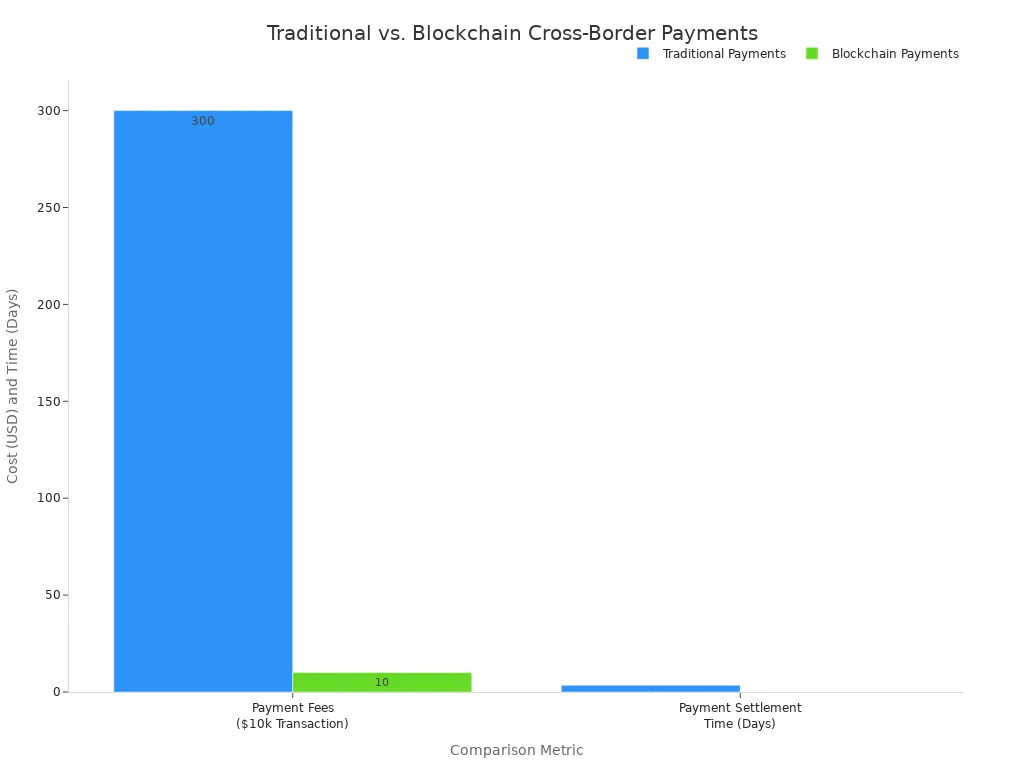
This use of blockchain technology improves the entire supply chain. The blockchain provides superior tracking capabilities.
Enhancing Data with the Power of AI

While blockchain provides a secure record, artificial intelligence (AI) gives that data meaning. AI algorithms analyze the vast information stored on the blockchain. This process turns raw data into predictive insights, which is essential for modern supply chain management. The synergy between AI and blockchain allows brands to anticipate future shocks, flag sustainability risks, and achieve greater supply chain efficiency. These advanced AI solutions are key to building a resilient and intelligent supply chain.
Turning Raw Data into Actionable Insights
AI excels at identifying patterns that humans might miss. It analyzes blockchain data alongside market trends and social media activity to improve demand forecasting. This capability is crucial for reducing overproduction. For example, AI-powered forecasting helps brands avoid creating excess inventory, which directly addresses waste. H&M Group, using AI technology, successfully cut overproduction by 30% in a single year. This demonstrates the power of AI in creating more sustainable and profitable ai-driven operations. The use of AI is transforming supply chain management.
Effective AI solutions help protect the global supply chain from disruptions. Predictive analytics can foresee potential bottlenecks like material shortages or shipping delays. This allows companies to adjust their strategies proactively, preventing costly interruptions. This level of foresight leads to major supply chain optimization and boosts overall efficiency. The combination of AI and blockchain is vital for managing complex supply chain disruptions.
Verifying Materials with Computer Vision
AI also provides powerful tools for physical verification. Computer vision, a field of AI, can confirm the authenticity of materials recorded on the blockchain. The process is straightforward and effective.
- First, AI-enabled cameras capture high-resolution images of a fabric's texture and fibers.
- Next, deep learning models extract unique features like weave density and color tone.
- Finally, the AI compares these features against a verified database stored on the blockchain.
This technology can detect inconsistencies and confirm a material's origin and composition. For instance, AI can verify if a yarn is truly organic cotton or contains hidden synthetic fibers. This application of AI ensures the data on the blockchain is accurate from the very start of the supply chain. It closes the loop between the digital record on the blockchain and the physical product, preventing fraud and enhancing supply chain management during potential disruptions.
The Impact of Traceable Sourcing by 2025
By 2025, the fusion of blockchain and AI will move traceable sourcing from a niche concept to an industry standard. This technological shift creates unprecedented transparency for both brands and consumers. It establishes a new foundation for trust and accountability in fashion. The impact will redefine product value, brand integrity, and consumer relationships.
Achieving End-to-End Transparency
End-to-end transparency allows brands to definitively prove their claims. The immutable ledger of blockchain provides a secure record, while AI analyzes this data for verification. This combination gives brands powerful tools to build credibility and operational excellence.
A primary benefit is the ability to guarantee product authenticity. Each item receives a unique digital identity on the blockchain. This creates a tamper-proof system for tracking a product from its origin. Brands use AI-powered tools to monitor online marketplaces for counterfeit products. This proactive approach protects brand reputation and revenue. For many shoppers, this is critical, as 56% of consumers state that authentication is a top priority. This system of real-time tracking and verification builds immense trust.
This level of visibility also helps brands combat greenwashing. Companies can no longer make vague sustainability claims. Instead, they can present verifiable data about their materials and processes. Platforms like TextileGenesis and Retraced enable this supply chain transparency. They connect thousands of suppliers and brands, using blockchain to ensure the provenance of materials. This technology provides the hard evidence needed to back up ethical and environmental commitments.
| Provider Name | Core Function for Transparency |
|---|---|
| Renoon | Manages green claims and launches Digital Product Passports. |
| The ID Factory | Specializes in chain of custody verification for footwear. |
| TrusTrace | Enables raw material tracking and impact assessment. |
| FairlyMade | Connects brands with ethical suppliers for better labor monitoring. |
Furthermore, this transparency directly supports the circular economy. Brands like Eileen Fisher use traceability to verify their use of sustainable materials, such as GRS-certified recycled fibers. Tesco is piloting digital passports for its F&F clothing line to inform consumers about circular practices. Leaders see the value here, with 74% recognizing that circular business models are profitable. The data from blockchain and AI systems provides the foundation for effective take-back programs, resale platforms, and recycling initiatives.
Empowering Consumers with Verifiable Data
The modern consumer is increasingly skeptical. Research shows that 80% of shoppers distrust brand transparency, and 54% do not believe the sustainability claims made by fashion companies. Verifiable data delivered through blockchain and AI directly addresses this lack of trust.
Imagine the shopping experience in 2025. A consumer picks up a jacket. They scan a QR code on the label with their phone. Instantly, the garment's entire story unfolds on their screen. This is already happening with brands like PANGAIA and Gabriela Hearst, who use QR codes to reveal a product's journey. The digital passport, powered by blockchain and organized by AI, provides clear, verifiable information.
This digital passport offers a comprehensive look at the product's lifecycle. It closes the information gap between the brand and the buyer, creating a new level of connection and confidence.
A study by the EPRS suggests what this digital passport will contain. The data gives consumers a complete picture of what they are buying.
- Product Description: General characteristics and size.
- Composition: Material percentages and dyeing processes.
- Supply Chain: Details on all manufacturing stages.
- Transport: Distances and methods used in shipping.
- Documentation: Certificates and audit reports.
- Environmental Impact: The product's carbon footprint data.
- Social Impact: Information on labor conditions.
- Impact on Animals: Details on animal welfare.
- Circularity: Information on recycled content and repair services.
- Health Impact: Data on hazardous substances.
- Information on the Brand: The brand’s sustainability goals.
- Communication/Identification Media: The QR code or NFC chip itself.
- Quantity: Production volume information.
- Costs: Optional disclosure of manufacturing costs.
- Usage and Customer Feedback: Optional consumer reviews.
- Tracking and Tracing After Sales: Data on the product's post-sale life.
This depth of information empowers consumers to make choices that align with their values. They can see the carbon footprint, verify the authenticity of the material, and confirm ethical production. This use of AI and blockchain for tracking and data delivery transforms a simple purchase into an informed decision, fostering genuine brand loyalty and trust.
Overcoming Challenges for Widespread Adoption
While the promise of traceable sourcing is immense, widespread adoption faces significant hurdles. The path to full transparency requires overcoming complex technical and financial barriers. Both technology and industry-wide cooperation are essential for progress.
The Hurdle of Integration and Standards
A primary challenge is technical integration. The fashion supply chain often relies on disconnected legacy systems not built for blockchain technology. This creates data silos that prevent the clean, unified information that both blockchain and AI require for effective tracking. Furthermore, different blockchain platforms often cannot communicate with each other. This lack of interoperability creates isolated systems and limits efficiency.
The fact that blockchains operate in isolation makes it difficult for companies to fully benefit from blockchain technology. ... True inter-platform interoperability ... would require developing the “one API/protocol to rule them all” and getting every platform to adopt that, consistently.
Technology alone is not a silver bullet for building trust. Stronger industry regulations and data standards are necessary to ensure true accountability. Global standards like the GS1 Global Traceability Standard (GTS) provide a blueprint for how to capture and share data. At the same time, new laws like the EU’s Corporate Sustainability Due Diligence Directive (CSDDD) and the proposed New York Fashion Act compel companies to address human rights and environmental impacts. This combination of blockchain technology and regulation pushes the industry toward genuine trust. The integration of AI with blockchain technology is key.
Making Traceability Scalable and Accessible
Cost presents another major barrier. Implementing comprehensive blockchain solutions can be expensive, with costs sometimes reaching millions of dollars. Many small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) in the fashion supply chain lack the resources for such advanced traceability systems. The high cost of blockchain technology adoption and training can be prohibitive for these smaller businesses.
Fortunately, new initiatives are making this technology more accessible. Digital platforms are emerging to bridge the gap between remote artisans and global brands. These tools improve efficiency and create direct connections, cutting out intermediaries.
- B2B platforms like World Collective help brands find authentic, certified artisanal materials.
- This approach gives smaller suppliers a wider customer base.
- It also provides emerging brands access to unique crafts without massive investment in blockchain technology.
These platforms use AI and blockchain technology to simplify tracking and verification. This makes the benefits of blockchain technology and AI integration available to more players, fostering a more inclusive and transparent ecosystem. The future of blockchain technology depends on these accessible blockchain solutions. This will build greater trust.
By 2025, traceable sourcing is no longer a niche concept. The synergy of blockchain and AI marks a turning point for the industry. This combination empowers consumers with verifiable data and protects brands with enhanced transparency. The use of blockchain builds radical trust.
This revolution in progress moves fashion beyond simple claims. The integration of blockchain and AI provides the verification needed for true transparency, creating a new foundation of trust.
This new era of accountable fashion relies on the traceability that blockchain provides. The future is built on the end-to-end transparency delivered by blockchain and AI technology.
FAQ
What is a digital passport in fashion?
A digital passport is a unique record for a garment. It uses blockchain to store verifiable data about a product's journey. Consumers can scan a code to see its material origin, production history, and environmental impact, creating radical trust and transparency.
How does blockchain prevent greenwashing?
Blockchain creates an unchangeable record of a product's supply chain. Brands must provide verifiable proof for their sustainability claims. This system makes it difficult to mislead consumers with false environmental marketing, as all data is transparent and permanent.
What is the main role of AI in traceable sourcing?
AI analyzes the vast data stored on the blockchain. It turns this raw data into actionable insights for brands. Key functions include:
- Predicting supply chain disruptions.
- Verifying material authenticity with computer vision.
- Improving demand forecasting to reduce waste.
Is this technology only for luxury brands?
No, traceability is becoming more accessible. While initial costs can be high, new platforms are emerging. These platforms help smaller brands and suppliers use blockchain and AI. This makes transparent sourcing possible for businesses of all sizes, not just luxury labels.
See Also
Transforming Traditional Apparel: Strategic Paths from Production to Brand Success
Balancing Fashion's Flow: Predictive Analytics for Supply and Demand
AI Sensors' Impact on the 2025 Fashion Supply Chain
Innovative AI Solutions for Sustainable Fashion and a Greener Planet
Streamlining Fashion Returns: Smarter AI Solutions for Immediate Impact