
Artificial intelligence (AI) is transforming fair labor oversight. It shifts the discipline from reactive to proactive. AI tools help companies manage complex global supply chain risks. These advanced tools improve supply chain compliance. The need for better oversight is clear.
The International Labor Organization estimates 40.3 million people are in modern slavery. This is a staggering 5.4 victims for every 1,000 people globally.
AI offers solutions for the modern supply chain. AI enables continuous monitoring and boosts supply chain transparency. An AI can analyze data to find labor risks before they escalate, moving beyond periodic audits. This improves supply chain compliance and transparency.
Core AI Tools and Applications
Companies now use specific AI tools to improve supply chain ethics. These tools help them move from a reactive to a proactive stance on fair labor. They offer powerful ways to analyze data, monitor conditions, and increase transparency across the supply chain.
Predictive Analytics for Risk
Predictive analytics allow companies to forecast and prevent labor issues. AI models analyze diverse datasets to identify potential problems. These datasets include information on geopolitical instability, supplier financial health, and historical violations. The AI can flag high-risk suppliers before violations happen.
For example, an AI system might flag a supplier in a region with new, restrictive labor laws. This alert gives the company time to investigate and act, protecting workers and ensuring compliance.
This proactive approach is a core part of modern supply chain management. AI helps companies monitor supplier compliance with ethical standards. It uses data from supplier audits, labor reports, and even social media. This continuous analysis helps prioritize risks and direct resources effectively. Unilever, for instance, uses AI to predict which suppliers might violate environmental laws, a model easily adapted for labor practices.
Real-Time Anomaly Detection
AI enables the real-time monitoring of working conditions. It processes continuous data streams from many sources. These sources include worker feedback platforms, social media, and Internet of Things (IoT) devices on the factory floor. This constant flow of information helps companies spot anomalies as they occur.
- Worker Count Monitoring: AI can enforce maximum worker counts in specific areas. This prevents overcrowding and reduces accident risks.
- PPE Compliance: Computer vision systems detect if workers are wearing required safety gear like helmets or gloves. The AI sends immediate alerts when it finds a violation.
- Work-Hour Patterns: An AI can analyze time-clock data. It alerts management to abnormal patterns, such as excessively long shifts or insufficient breaks, which may signal forced labor.
These tools provide a level of oversight that manual checks cannot match. The constant monitoring helps maintain a safe and fair work environment throughout the supply chain.
Enhanced Auditing with AI
AI also enhances traditional audits. Natural Language Processing (NLP) is a key technology in this area. NLP automates the analysis of unstructured data. This includes documents like audit reports, worker grievances, and supplier contracts. The AI can find hidden compliance issues that human auditors might miss.
NLP tools can perform several key tasks:
- Entity Recognition: It extracts specific information like names, locations, and dates from text.
- Sentiment Analysis: The AI detects emotions in worker feedback, identifying frustration or fear. This helps prioritize grievances based on emotional urgency.
- Topic Modeling: It groups large volumes of text into themes, revealing widespread issues across the supply chain.
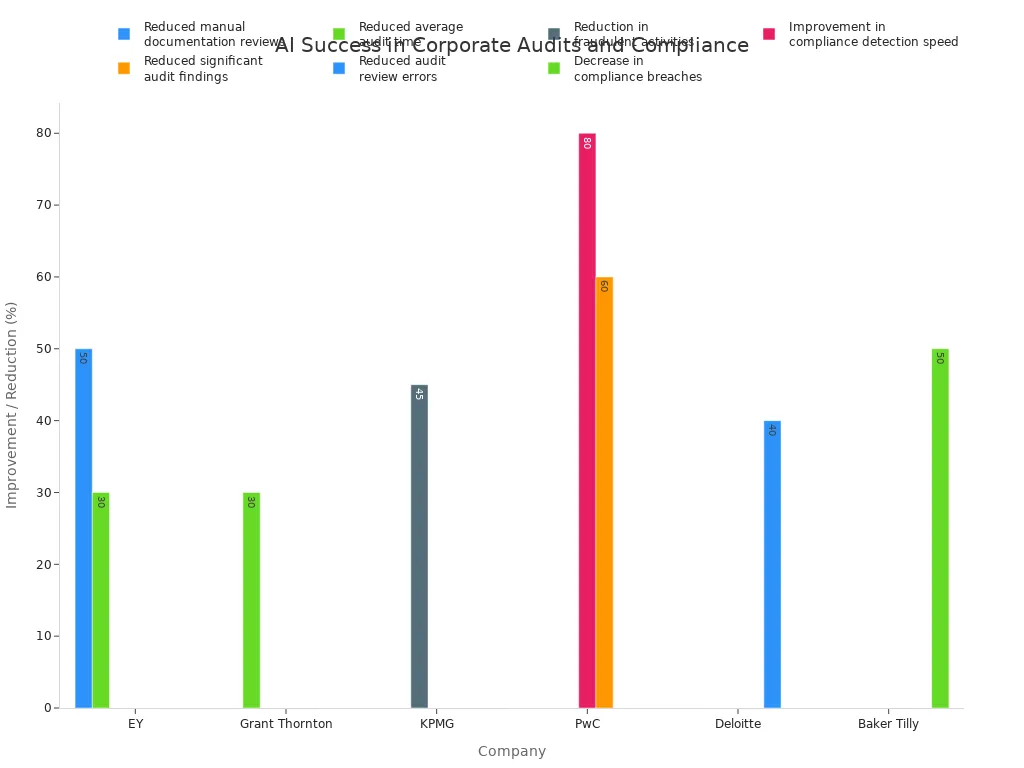
Many firms have seen success with these advanced tools. AI platforms have significantly improved the speed and accuracy of audits, leading to better ethical compliance.
| Company | AI Platform/Tool | Key Achievement in Compliance/Audit |
|---|---|---|
| EY | EY Helix | Reduced manual documentation reviews by 50% and average audit time by 30%. |
| KPMG | KPMG Clara | Improved fraud identification rates, with clients reporting up to a 45% reduction in fraudulent activities. |
| PwC | Halo platform | Achieved an 80% improvement in compliance detection speed. |
| Deloitte | Omnia platform | Reduced audit review errors by 40% by identifying patterns in large datasets. |
These AI tools find subtle patterns that indicate non-compliance. They can flag inconsistencies in data or identify departments that repeatedly fail to meet standards. This deep analysis strengthens supply chain ethics and corporate responsibility.
Boosting Supply Chain Transparency
Greater transparency is essential for ensuring fair labor practices. AI offers powerful transparency tools to connect all parts of the supply chain. Machine learning algorithms can directly match producers with buyers. This matching is based on verified fair labor practices and sustainability metrics. This process increases overall transparency and rewards ethical suppliers.
AI works with other technologies to build trust.
- AI and IoT: AI-powered sensors provide real-time data on goods, inventory, and worker safety. This helps prevent issues and builds a clear record of conditions in the supply chain.
- AI and Blockchain: Combining AI with blockchain creates a secure, tamper-proof record of all transactions. Starbucks uses this combination to verify its fair trade sourcing. The AI analyzes the blockchain data and flags any non-compliant suppliers.
This level of transparency empowers consumers and businesses. It creates a supply chain where ethical practices are visible and verifiable. Better transparency ultimately leads to better ethics and stronger compliance.
Challenges in Supply Chain Ethics

Adopting AI tools for fair labor oversight presents significant challenges. Companies must navigate complex issues to ensure these technologies improve supply chain ethics. Success depends on addressing data integrity, overcoming financial barriers, and managing human rights risks. These hurdles require careful planning and a commitment to ethical principles.
Data Integrity and Access
Reliable data is the foundation of any effective AI system. Acquiring trustworthy information from diverse global sources is a major challenge in supply chain management. Data from different regions may be inconsistent, incomplete, or intentionally falsified to hide violations like forced labor or unsafe working conditions. Building a secure data infrastructure is the first step toward better supply chain ethics.
Companies can implement several best practices to ensure data integrity. These measures protect sensitive worker information and build a foundation for reliable AI analysis.
- Data Validation: Implement checks during data entry to ensure accuracy.
- Access Control: Restrict data access to authorized personnel based on their roles.
- Data Encryption: Encrypt sensitive data during transmission and storage to prevent unauthorized access.
- Regular Backups: Perform frequent backups to restore data in case of loss.
- Audit Trails: Maintain detailed logs of data access and changes for monitoring.
Local partnerships are also crucial for gathering reliable data. They build trust and provide local context that an outside company might miss. For example, USAID partnered with Mars Petcare in Thailand to reduce labor exploitation in the seafood supply chain. This collaboration focuses on improving worker voice and responsible recruitment, strengthening ethical sourcing from the ground up.
These partnerships help local suppliers meet international compliance standards. They improve data accuracy and support certifications for fair labor practices. This approach strengthens the entire supply chain.
Technological and Financial Barriers
The high cost and complexity of AI implementation create significant barriers. Many small and medium-sized suppliers in a global supply chain cannot afford expensive software or the experts needed to run it. This financial gap can weaken the effectiveness of AI monitoring across the entire supply chain.
Beyond cost, other technological hurdles exist.
- Lack of Trust: Many businesses are uneasy about sending confidential data to cloud-based AI platforms. They worry about data breaches and the reliability of AI-generated results.
- Legacy Systems: Older IT systems often do not integrate well with modern AI tools. Replacing or integrating these systems is a complex and risky project.
- Skills Gap: A survey by the Institute of Directors found that 51% of business leaders lack knowledge about AI. This skills gap makes it difficult for companies to identify useful AI applications.
To overcome these barriers, companies can adopt more flexible strategies. Scalable cloud platforms offer a cost-effective way to access powerful AI tools without a large upfront investment. Companies can start with small pilot programs to demonstrate a return on investment. A successful pilot can build confidence and justify a larger rollout. This approach makes advanced technology more accessible to more partners in the supply chain.
Addressing Human Rights Risks
The use of AI in the workplace introduces serious ethical dilemmas. While AI can detect issues like forced labor, it also creates new human rights risks. Worker privacy is a primary concern. Constant monitoring can cross the line between work and private life, creating an environment of distrust.
The German regulator fined H&M $41 million for illegal surveillance. The company kept excessive records on employees' families, religions, and illnesses. This case highlights how monitoring can easily violate the fundamental right to privacy.
This level of surveillance can have a chilling effect on workers. They may fear retaliation for speaking up about poor conditions or attempting to organize. This fear undermines efforts to create transparency and can hide forced labor. Algorithmic bias is another major risk. AI systems trained on historical data can perpetuate and even amplify existing social biases.
| Bias Type | Example of Negative Impact |
|---|---|
| Gender Bias | An AI hiring tool trained on past data might favor male candidates, screening out qualified women. |
| Racial Bias | Speech recognition systems have shown higher error rates for Black users, creating barriers to using voice-activated tools. |
| Disability Bias | An AI monitoring desk breaks could unfairly penalize workers with physical disabilities who need more frequent rests. |
To manage these human rights risks, companies need strong governance. AI is a tool for insight, not a replacement for human oversight and corporate responsibility. Clear governance frameworks are essential for managing the ethics of AI. The OECD AI Principles and the NIST AI Risk Management Framework offer guidance on promoting transparency, fairness, and accountability. These frameworks help ensure that AI systems support human-centered values. Ultimately, human judgment must guide the use of AI to ensure true ethical compliance and protect workers throughout the supply chain.
AI tools empower companies to ensure fair labor practices. This proactive AI approach transforms supply chain ethics. AI offers continuous monitoring for the supply chain, a clear upgrade from periodic audits that miss risks. The effectiveness of these AI tools hinges on managing data, costs, and ethics. Better AI improves supply chain compliance and supply chain transparency. AI tools enhance supply chain transparency. AI is a powerful instrument for insight. AI provides data for better labor practices. AI improves compliance and transparency.
AI is a powerful instrument, but ultimate responsibility for fair ethics remains a fundamentally human endeavor.
FAQ
How does AI improve fair labor in a supply chain?
An AI system analyzes data from the supply chain. This AI helps companies find labor risks early. The AI can monitor work hours and safety compliance. This proactive approach helps protect workers. The AI provides insights for better supply management.
What are the main challenges of using AI for supply ethics?
Key challenges include poor data quality and high costs. Many supply partners lack the funds for advanced AI. Worker privacy is also a major concern. An AI can have biases, creating unfair outcomes. Companies must manage these risks carefully.
Can AI replace human auditors in the supply chain?
No, AI cannot fully replace human auditors. The AI is a powerful tool for analysis. It helps auditors work more efficiently.
However, human judgment is essential. People must interpret the AI findings and make final decisions to ensure true ethical compliance in the supply chain.
How does AI help small suppliers in the supply chain?
Cloud-based AI platforms offer affordable solutions. These tools help small suppliers meet global standards. The AI can simplify compliance reporting. This support allows them to participate in the global supply chain more easily. Better data from the supply chain benefits everyone.
See Also
Apparel Evolution: Strategic Paths from Manufacturing to Brand Success
TAGG Logistics 2024 Review: Smart 3PL Fulfillment for eCommerce Growth?
Boosting Efficiency: The Essential Impact of Warehouse Audits
Unlocking Revenue: AI-Powered Dynamic Pricing Strategies for Business Growth
Optimizing Resources: AI-Driven Capacity Planning for Modern Brands