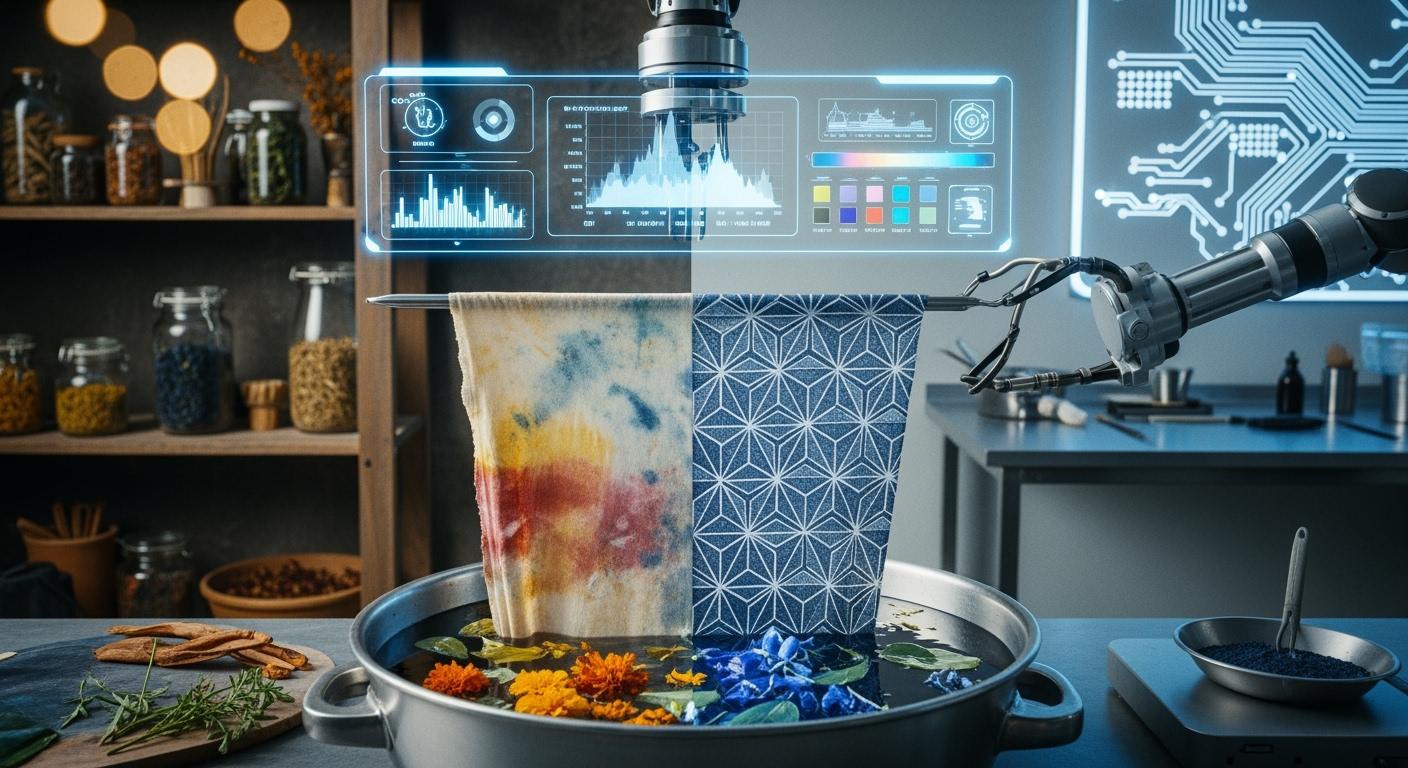

Artificial intelligence (AI) can replicate natural dye effects using generative algorithms. The AI analyzes large sets of images showing organic dye patterns and colors. This AI then generates unique digital designs for textile dyeing. Advanced printers apply these designs directly onto fabrics. This modern textile dyeing process allows manufacturers to replicate natural dye effects with precision and at a large scale. The role of AI in the dyeing industry is expanding quickly.
Market Insight: AI in Textiles A report from Technavio highlights the significant growth of AI. It forecasts market size and year-over-year growth for AI technology from 2024 to 2029.
How AI Can Replicate Natural Dye Effects

Artificial intelligence uses several advanced methods to achieve realistic natural dye aesthetics. These techniques focus on pattern creation, color accuracy, and texture simulation. This biomimetic approach allows AI to digitally mirror the organic beauty of traditional textile dyeing. The ML models learn from nature to create designs for modern manufacturing.
Generative Pattern Design
Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) are a key technology in this area. A GAN consists of two competing AI models. One AI, the generator, creates new fabric patterns. The other AI, the discriminator, judges if the patterns look authentic. This process trains the generator to produce highly realistic designs. The AI learns from thousands of images of fabrics dyed with sources like indigo or cochineal. It captures the subtle, imperfect details that make natural dyes unique.
This ML technique offers designers powerful new tools.
- GANs explore a vast range of new patterns, colors, and combinations.
- The AI helps designers create high-resolution fabric textures.
- It allows virtual experiments with different materials and patterns.
Major brands already use this technology. For example, the clothing retailer H&M has utilized GANs to develop new outfits for its product lines, showing the practical application of AI in fashion design.
Predictive Color Analysis
Achieving the right color is critical in textile dyeing. AI excels at predicting color outcomes with high precision. Hybrid ML models analyze how natural colorants like madder and weld will appear on different fabrics, such as cotton or polyester. The AI predicts the exact color coordinates, ensuring consistency across large production runs. This capability is essential for complex dyeing processes.
These ML systems can handle difficult dyeing challenges. For blended fabrics like cotton/polyester, different fibers absorb dye differently. AI models predict these variations in dye uptake. They then formulate an optimal dye recipe to achieve a uniform shade. This removes guesswork from the dyeing process.
Tech Note: AI Models for Color Prediction Several types of AI and machine learning models power color analysis. These include Artificial Neural Networks (ANNs), deep learning algorithms like CNNs, and optimization methods like Particle Swarm Optimization. These advanced ML tools improve the efficiency and accuracy of color matching in textile dyeing.
Simulating Fabric Textures
AI can also forecast how a pattern will look on a specific fabric. The technology simulates dye uptake on different material structures. It predicts how a design would appear on various weaves, from a simple plain weave to a complex satin. This allows designers to replicate natural dye effects like Japanese shibori, where patterns are created by folding and binding fabric. The AI can mimic how the dye would pool in some areas and be resisted in others.
AI-powered virtual simulation tools are fundamental to this process. These tools let designers see how a fabric will drape, move, and stretch in a virtual environment. An Artificial Neural Network (ANN) can use the weave type as an input to predict fabric properties. This foundational capability of AI allows it to forecast the final visual appearance of a pattern on any textile. This ML simulation ensures the digital design translates perfectly to the physical product, completing the effort to replicate natural dye effects.
The AI-Powered Dyeing Process

The AI-powered dyeing process transforms textile manufacturing through a structured, four-stage workflow. This method combines data science, creative design, advanced printing, and automated quality assurance. Each step uses AI and ML technologies for process optimization and superior results in textile dyeing. This systematic biomimetic approach ensures the final product faithfully replicates the beauty of natural dyes.
Data Collection and Training
The journey begins with extensive data collection. Technicians gather thousands of high-resolution images of fabrics colored with natural dyes. This dataset includes a wide variety of patterns, textures, and color variations. The AI then analyzes these images during a training phase. A machine learning model, often a Generative Adversarial Network (GAN), learns the unique characteristics of organic dyeing. The ML model studies subtle imperfections, color bleeds, and textural effects. This foundational step enables the AI to understand the essence of natural dyeing processes. The quality of this initial data directly impacts the authenticity of the final designs.
AI-Assisted Design Generation
Once the ML model is trained, designers use AI-driven solutions to create new patterns. These platforms act as powerful creative partners, enhancing efficiency and personalization. AI-powered tools can generate unique patterns from simple text descriptions or reference images. This serves as a rapid idea engine for concept development.
Several industry-leading software platforms facilitate this stage:
- CLO 3D allows designers to create realistic 3D garments and simulate how different fabrics drape and fit. Its AI assistant and physics engine help designers test materials virtually.
- Style3D AI specializes in fabric visualization. It uses AI for realistic texture rendering and automatic stitching adjustments.
- The New Black and Ablo AI help designers generate fashion visuals and entire apparel collections from mood boards or sketches.
This AI-assisted workflow dramatically speeds up the design cycle. Brands like Moncler use AI to innovate quilted textures, while Tommy Hilfiger has engaged customers in generative design. The efficiency gains are significant.
| Workflow Phase | Traditional Time | AI-Assisted Time |
|---|---|---|
| Design Discovery | 1–3 Weeks | Under 1 Week |
| UI Prototyping | 2 Days | 25 Minutes |
| Requirement to Prototype | 2–3 Days | 3 Hours |
An AI copilot offers a major productivity gain because it compresses the feedback cycle. One user noted, “Where it really saved time was in the architecture phase... That alone probably saved me six to eight hours.” This acceleration allows for rapid prototyping and faster market entry. The ML models provide a major boost to process optimization.
Digital-to-Fabric Printing
After finalizing a design, the next step is printing it onto fabric. The AI-powered dyeing process uses advanced digital-to-fabric printers. These machines translate the complex, AI-generated digital files into physical textiles with remarkable precision. To capture the fine details of natural dye effects, a minimum image resolution of 300 DPI is necessary. High-end giclée prints often use 1200 DPI or higher for smooth gradients and sharp details.
Modern digital printers offer advanced capabilities for textile dyeing:
- Printers with 8 or 10 color channels provide an expanded color gamut.
- Specialty inks, including neon and metallic options, create unique visual effects.
- Advanced Raster Image Processor (RIP) software manages color profiles and print queues.
Printers like the HPRT DA182T Plus Dye Sublimation Textile Printer are built for this task. It uses industrial printheads to print up to 650 square meters per hour on polyester fabrics. This technology maintains high resolution without sacrificing fabric softness. Furthermore, digital printing is more energy-efficient than traditional dyeing. It uses almost no water and involves a simpler post-treatment process, reducing overall energy consumption. Many machines are also IoT-enabled, allowing for the real-time monitoring of the dyeing operation. This real-time monitoring helps maintain consistent output.
Quality Control and Finishing
The final stage of the AI-powered dyeing process ensures product quality and durability. Automated Optical Inspection (AOI) systems use AI to check the printed fabric for defects. These systems employ deep learning models, such as Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs), to perform quality control. The ML models are trained on large datasets of flawless and defective fabrics. This training allows the AI to identify tears, holes, printing errors, and subtle texture variations that human inspectors might miss. This automated quality control provides real-time monitoring of production.
After inspection, the fabric undergoes finishing treatments to enhance its properties. These processes are crucial for ensuring the longevity of the digitally printed textile. Standard finishing options include:
- Heat Setting: A thermal process that stabilizes synthetic fibers to prevent wrinkles and shrinkage.
- Waterproofing: A chemical coating that repels water, ideal for outdoor textiles.
- UV Protection: A functional finish that shields fabric from sun damage.
- Anti-Microbial Treatment: A hygienic finish that prevents bacterial growth and odors.
These AI and ML-driven steps in textile manufacturing ensure a high-quality, durable, and aesthetically pleasing final product that successfully mimics natural dyeing.
Core Benefits of This AI Approach
Adopting AI for textile dyeing offers major advantages over traditional methods. This technology improves production efficiency, reduces environmental harm, and unlocks new creative possibilities. The AI-driven solutions provide a clear path toward modernizing the textile industry with a focus on quality and sustainability.
Consistency and Scalability
AI ensures consistent quality across large production runs. Traditional dyeing often produces variations, but AI systems create uniformity. They use real-time data to maintain standards. This AI approach boosts production efficiency and guarantees a reliable final product.
How AI Maintains Quality An AI system uses several methods to ensure consistent dyeing results:
- It analyzes real-time sensor data to make dynamic recipe adjustments.
- It uses automated anomaly detection to flag subtle drifts from optimal performance.
- AI performs root cause analysis to quickly identify and fix machine issues.
- It establishes smart benchmarks to flag problems and start corrections automatically.
Environmental Impact Reduction
The AI-powered dyeing process significantly lowers the industry's environmental footprint. Traditional dyeing processes consume vast amounts of resources. Digital printing with AI offers powerful sustainable solutions. It drastically cuts water usage, chemical waste, and energy consumption. This focus on sustainability is a core benefit of modern textile dyeing. AI also forecasts color fastness, which helps minimize failed batches and further reduces waste.
| Resource/Metric | Traditional Screen Printing | Digital Textile Printing |
|---|---|---|
| Ink Usage (per meter) | 35–60 cc | 6–9 cc |
| Factory Space | Over 5,000 sq ft | Under 400 sq ft |
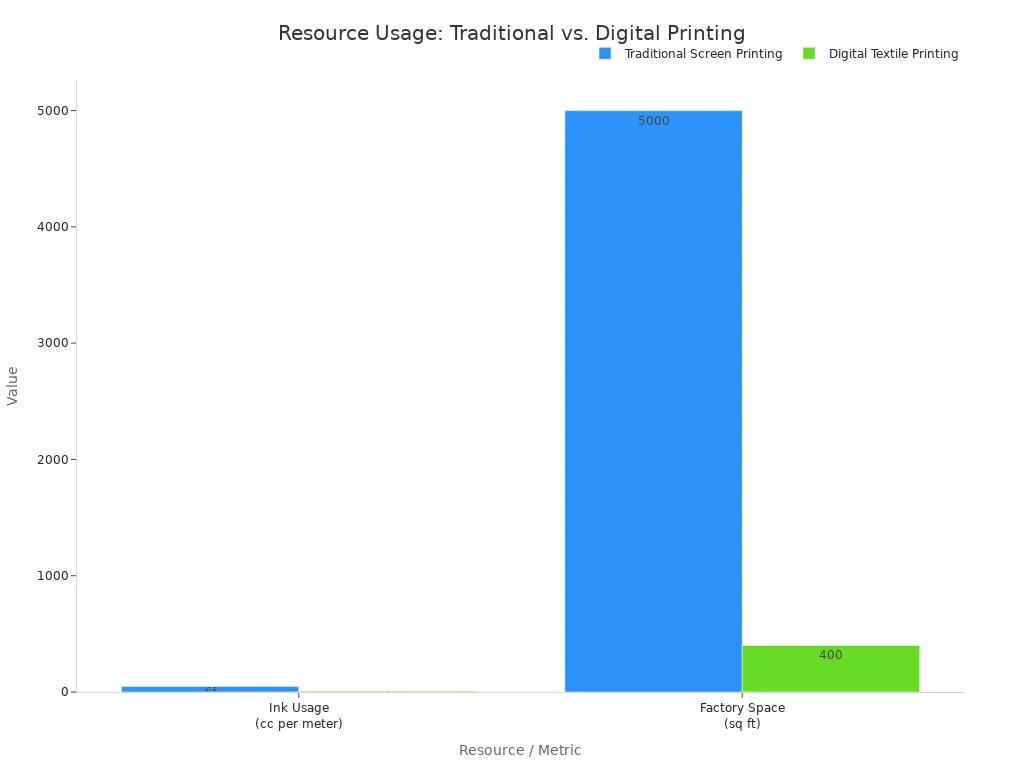
This improved efficiency in dyeing makes AI a key tool for sustainability.
Expanded Creative Freedom
AI gives designers unprecedented creative freedom and efficiency. It accelerates the journey from concept to final product. Designers can generate hundreds of variations quickly. This allows for rapid prototyping and greater customization. AI tools help create customized textiles that meet specific consumer demands. This technology transforms the creative workflow in textile dyeing.
- Rapid Prototyping: AI can generate many design variations for a single garment.
- Cost Reduction: The technology removes the need for many physical samples.
- Virtual Try-Ons: AI and AR apply designs to digital models for instant visualization.
- Improved Decisions: Designers can make data-driven choices based on visual previews.
This AI-powered efficiency allows brands to test ideas and respond to market trends faster than ever before.
Artificial intelligence (AI) offers a powerful, scalable, and sustainable method to replicate natural dye effects. This technology successfully merges the beauty of organic patterns with the precision of digital production. The AI assists designers but does not replace human creativity. Instead, AI enhances the creative process. The future of AI in the industry looks even more promising.
Future of Sustainable AI
- Waste Reduction: AI algorithms will pinpoint and reduce material waste.
- Energy Monitoring: AI will track and optimize energy usage in factories.
- On-Demand Production: AI enables manufacturing only what is needed, cutting overproduction.
This approach paves the way for a new era in textile manufacturing.
FAQ
Does AI replace human designers in this process?
No, AI does not replace human designers. It acts as a powerful tool. The technology enhances a designer's creativity and efficiency. Designers guide the AI to produce the final patterns, making creative decisions throughout the process.
What is the main environmental benefit of AI dyeing?
The primary environmental benefit is sustainability. AI-guided digital printing uses almost no water compared to traditional vat dyeing. This modern textile dyeing method also significantly reduces chemical waste and energy consumption, making it a greener alternative.
Can AI replicate any type of natural dye effect?
Yes, AI can replicate a wide range of effects. It analyzes thousands of images to learn the unique patterns of dyes like indigo or shibori. The system then generates new digital designs that mimic these organic and imperfect aesthetics with high accuracy.
Is this technology accessible to smaller brands?
Yes, this technology is becoming more accessible. Many AI software platforms offer services that smaller brands and independent designers can use. This allows them to compete with larger companies by creating unique, customized textiles without needing a massive factory.
See Also
Sustainable Fashion AI: Innovative Solutions for a Greener Planet
AI's Role in Managing Viral Trends Within Fast Fashion
Optimizing Fashion Returns: Smarter AI Solutions for Efficiency
Dynamic Safety Stock AI: Revolutionizing 2025 Fashion Retail Solutions
Machine Learning: Predicting Fashion Trends to Significantly Boost Sales