
Autonomous procurement planning revolutionizes raw material sustainability. This system uses AI to automate sustainable procurement decisions, addressing the significant impact of supply chains. These activities often represent 75% of a company's total emissions. The AI moves beyond manual procurement checks, creating a dynamic supply chain. This AI-powered automation actively improves sustainability through better ethical sourcing and ESG compliance. It makes complex procurement goals both achievable and measurable, transforming how businesses approach their environmental responsibilities.
Understanding Autonomous Procurement Planning
Autonomous procurement planning uses advanced technology to automate and optimize purchasing decisions. It creates a system that thinks, learns, and acts on its own to meet strategic goals. This approach transforms procurement from a manual, reactive process into a proactive, data-driven function.
Defining the Core Concept
At its core, autonomous procurement planning is an evolution beyond traditional methods. It represents a shift toward intelligent purchasing systems that operate with minimal human intervention. The system uses AI to analyze data, predict needs, and execute procurement tasks. This automation frees professionals to focus on strategic oversight and supplier relationships. The fundamental differences are clear when comparing the two approaches.
| Feature | Traditional Procurement | Autonomous Procurement |
|---|---|---|
| Process Initiation | Shipper posts load on bidding platform | System predicts acceptable carrier offers |
| Carrier Action | Carriers analyze load and submit bids | Carriers receive predicted offers |
| Decision Making | Shipper waits for bids, then selects | First carrier to accept gets awarded instantly |
| Carrier Experience | Uncertainty of award after bidding | Instant award, making it more attractive |
This new model delivers significant advantages:
- Enhanced Decision-Making: AI agents continuously analyze data to identify cost patterns and flag supplier risks.
- Increased Efficiency: Real-time data processing leads to faster supplier selection and shorter procurement cycles.
- Strategic Focus: Teams shift from routine tasks to high-value initiatives like governance and relationship management.
The Role of AI Agents and Generative AI
AI agents are the engines driving autonomous procurement. These specialized AI programs are designed to achieve specific goals. Unlike other forms of AI, AI agents possess a higher degree of autonomy and adaptability. They do not simply follow pre-set rules; they make probabilistic decisions to achieve the best outcome.
| Characteristic | Generative AI Chat | RPA Bots | AI Agents |
|---|---|---|---|
| Trigger | Human prompt | Pre-set rules | Defined goals |
| Adaptability | Limited | None | High |
| Decision logic | None | Deterministic | Probabilistic + rules |
The capabilities of AI agents make them ideal for complex procurement environments. These AI agents can:
- Set goals: AI agents interpret objectives like 'reduce Scope 3 emissions' and work independently to meet them.
- Observe their environment: They monitor internal data and external market conditions to respond proactively.
- Reason with data: AI agents evaluate multiple variables like price, quality, and supplier reliability to simulate logical thinking.
- Interact with other systems: They automate tasks by soliciting quotes from suppliers and awarding business based on defined criteria.
- Learn independently: These AI agents analyze outcomes to improve future decisions and provide prescriptive recommendations.
For example, if weather delays a shipment, AI agents can reroute it or adjust sourcing strategies in real time. By constantly monitoring performance, AI agents help mitigate supplier risk and make informed decisions faster than human teams. These powerful AI agents streamline supplier selection, automate contract management, and improve demand forecasting. The AI agents are not just tools; they are decision-makers that learn and evolve.
Key Technologies: AI, Blockchain, and IoT
A successful autonomous procurement system integrates several key technologies. Each plays a distinct but complementary role in building a resilient and sustainable supply chain.
Note: These technologies work together. AI provides the intelligence, IoT provides the real-time data, and blockchain provides the trust and transparency.
-
Artificial Intelligence (AI) The AI is the brain of the operation. It processes vast amounts of data from various sources to enable data-driven decisions. AI algorithms handle complex tasks like dynamic contract and pricing intelligence, risk assessment, and demand forecasting. This intelligence allows the procurement system to optimize for cost, speed, and sustainability simultaneously.
-
Blockchain Blockchain technology provides an immutable and transparent digital ledger. In procurement, it creates a permanent, auditable record of every transaction from raw material to finished product. This capability is crucial for sustainability.
- Product Traceability: It creates a single source of truth to verify a material's origin and journey.
- Ethical Sourcing: It helps verify compliance with labor standards and environmental regulations.
- Quality Assurance: It validates compliance at every production stage without extensive manual checks.
-
Internet of Things (IoT) IoT devices act as the system's eyes and ears. Sensors placed on inventory, in warehouses, and on shipments provide a constant stream of real-time data. This information feeds directly into the AI for immediate analysis and action.
- Real-time Inventory: Sensors provide immediate stock level updates, triggering automatic reorders to prevent shortages.
- Supply Chain Transparency: GPS-enabled sensors track shipments, offering accurate delivery timelines.
- Automated Quality Control: Integrated sensors perform real-time quality checks during manufacturing.
Enhancing Sustainability with Autonomy

Autonomous systems transform sustainability goals from abstract targets into measurable outcomes. They achieve this by embedding ESG criteria directly into the procurement process. This integration allows companies to make smarter, more responsible decisions automatically. The result is a supply chain that actively works to reduce its environmental impact.
Automating Sustainable Procurement
Effective supplier management is the foundation of sustainable procurement. AI agents automate the complex task of vetting suppliers. These AI agents analyze vast amounts of data against a company's specific ESG goals. They scan public records, news, and social media to assess a supplier's reputation and practices. This automation significantly reduces the time needed for manual vetting.
AI evaluates suppliers on key ESG metrics. It checks for certifications like the Forest Stewardship Council (FSC) and verifies compliance with labor standards. Companies using AI for supplier evaluation have seen a 25% improvement in ESG compliance rates. This proactive approach helps mitigate risks tied to regulatory fines and brand damage. The AI agents provide an objective assessment of a supplier's sustainability practices by analyzing:
- Certifications and regulatory compliance
- Energy usage and water consumption
- Waste production and carbon emissions
This data-driven process removes human bias from supplier selection. It ensures that procurement decisions align with corporate sustainability commitments. The AI provides continuous monitoring, replacing periodic manual reviews with real-time performance tracking.
Dynamic Logistics Optimization
Logistics contribute significantly to a company's carbon footprint. Autonomous procurement planning addresses this by optimizing transportation dynamically. AI agents use advanced algorithms to find the most efficient shipping routes. They continuously recalculate paths based on real-time data like weather, traffic, and port congestion.
These systems employ several types of algorithms to minimize fuel consumption and emissions:
- Classical Solvers: Algorithms for the Vehicle Routing Problem (VRP) find the most efficient initial routes.
- Metaheuristics: Methods like Genetic Algorithms manage complex scenarios with multiple constraints.
- Machine Learning Models: These models learn from historical and live data to predict travel times and avoid delays.
Beyond route planning, AI agents also consolidate shipments. They identify opportunities to combine smaller loads into a single, full truckload. This intelligent purchasing strategy reduces the number of vehicles on the road. The result is a direct reduction in Scope 3 emissions and a more cost-effective logistics operation.
Full Traceability with Supply Chain Mapping
Verifying a material's origin is critical for sustainability. Autonomous systems use blockchain and IoT to create a fully traceable supply chain. IoT sensors on raw materials and shipments gather real-time data. This information includes location, temperature, and humidity. Blockchain technology then records this data on an immutable digital ledger.
Once data is on the blockchain, no one can alter it. This creates a tamper-proof record of a product's journey from its source to the final consumer. This technology is essential for ethical sourcing and compliance. It allows companies to:
- Verify certifications for Fair Trade or organic materials.
- Track products to confirm they do not come from regions linked to deforestation.
- Deter fraud and unethical practices with transparent, auditable records.
| Company/Organization | Industry/Product | Traceability Approach |
|---|---|---|
| The Hershey Company | Confectionery (Cocoa) | Uses a visualization platform to map factories and suppliers. |
| Circulor | Tantalum Ore | Built a blockchain system for mine-to-product traceability. |
| Nike | Apparel & Footwear | Maintains a map of factories and material suppliers. |
Predictive Analytics for Waste Reduction
Over-ordering raw materials leads to significant waste and financial loss. AI-powered predictive analytics prevent this problem. The AI analyzes historical data and market trends to forecast demand with high accuracy. This allows procurement teams to order exactly what is needed, minimizing excess inventory.
The process involves several steps:
- Data Collection: The system gathers historical sales data, supplier lead times, and seasonal trends.
- Modeling: Machine learning algorithms process the data to identify patterns and build predictive models.
- Application: The insights guide restocking schedules and production plans. A forecasted spike in demand can trigger early reorders to prevent stockouts.
Tip: To be effective, these predictive models require a wide range of data inputs. This includes real-time inventory levels, promotional schedules, product life cycles, and even customer sentiment analysis.
By removing guesswork, predictive analytics helps businesses match supply with actual demand. This data-driven approach to procurement not only reduces material obsolescence but also makes the entire supply chain more resilient and efficient. The impact on sustainability is clear: less waste means a smaller environmental footprint.
Your Autonomous Procurement Workflow

Adopting an autonomous procurement workflow transforms how a company approaches sustainability. This structured process embeds ESG principles into daily operations. It provides a clear path from defining goals to achieving measurable results. The entire workflow relies on AI agents to execute tasks and optimize decisions.
Step 1: Define Your Sustainability KPIs
A successful strategy begins with clear, measurable goals. Companies must define specific Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) for sustainability. These KPIs guide the AI agents and provide a benchmark for success. Vague objectives are not enough; the system needs concrete targets to optimize procurement decisions.
Example Goals: A company might aim to "reduce Scope 3 emissions by 15%" or "source 80% of materials from suppliers with recognized ESG certifications."
Effective ESG KPIs provide a framework for the AI agents. They translate broad corporate values into actionable procurement rules. Key metrics often include:
- Total GHG Emissions: Tracking the sum of Scope 1, 2, and 3 emissions to measure the complete carbon footprint.
- Waste Reduction Rate: Calculating the percentage of waste diverted from landfills.
- Ethical Sourcing: Auditing suppliers against fair labor standards and corporate codes of conduct.
- Recycled Content: Mandating a minimum percentage of recycled materials in purchased goods.
Well-respected certifications simplify complex sourcing decisions. They help companies select suppliers more efficiently. Benchmarking against industry standards, like those for sustainable materials, helps track progress and identify opportunities for improvement in supplier management. These defined ESG targets are the foundation of an intelligent procurement system.
Step 2: Integrate Critical Data Sources
AI agents require a constant flow of high-quality data to make informed decisions. An effective autonomous system connects and synthesizes information from multiple sources. This integration creates a complete picture of the supply chain, enabling the AI to analyze performance, predict disruptions, and act proactively.
Key data sources to integrate include:
- Internal Systems: Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems and supplier databases provide foundational data on spending, contracts, and performance.
- Supplier Data: Direct feeds from suppliers offer real-time information on inventory levels and production capacity.
- Third-Party Platforms: Services that rate suppliers on ESG performance provide crucial external validation for sustainability claims.
- IoT Sensor Data: Devices on shipments and in warehouses deliver live updates.
IoT data is especially valuable for logistics and quality control. AI agents use this information to optimize routes and ensure compliance.
| Data Source | Information Provided | Use Case for AI Agents |
|---|---|---|
| GPS Sensors | Real-time location, traffic data | Dynamic route optimization to reduce fuel |
| Temperature Beacons | Shipment temperature, humidity | Quality control for sensitive materials |
| Fleet Monitors | Average fuel consumption | Calculating and reducing Scope 3 emissions |
This comprehensive data integration allows the AI to move beyond simple automation. It empowers the AI agents to make complex, context-aware decisions that align with a company's ESG goals.
Step 3: Configure AI-Powered Purchasing Automation
With goals defined and data integrated, the next step is to configure the technology. This involves selecting the right platform and setting up the decision-making rules for the AI agents. The choice of an AI-powered purchasing automation platform is critical for long-term success.
Key criteria for selecting a platform include:
- Integration Capabilities: The platform must connect seamlessly with existing ERP and accounting systems.
- Usability: A user-friendly interface is essential for team adoption and effective workflow management.
- Scalability: The system should be able to grow with the business and handle increasing complexity.
- Cost-Benefit Analysis: A clear return on investment (ROI) must be evident, factoring in savings from efficiency and improved ESG compliance.
Once a platform is chosen, procurement teams configure the decision logic. They translate the ESG KPIs from Step 1 into automated rules. For example, an AI agent can be instructed to prioritize suppliers with high ESG ratings or automatically disqualify those who fail to meet specific emissions targets. This AI-powered purchasing automation ensures every procurement decision actively supports the company's sustainability objectives. This configuration is central to effective supplier management.
Step 4: Pilot, Monitor, and Scale
Implementing a new system requires a careful, phased approach. A pilot program allows a company to test the autonomous procurement workflow in a controlled environment. This minimizes risk and helps fine-tune the system before a full-scale rollout. The pilot should focus on a specific category with clear specifications.
A successful pilot program follows several key stages:
- Establish a Baseline: Document current performance metrics, including cycle time, costs, and ESG compliance.
- Define Pilot Scope: Select a manageable procurement category and document the rules for the AI agents. Clarify when an AI agent can act alone versus when it needs human approval.
- Conduct the Pilot: Run a set number of end-to-end procurement events using the new system.
- Measure Performance: Track key metrics to compare the pilot's results against the baseline. Success metrics often include faster sourcing cycles, cost savings, and improved compliance. User satisfaction surveys are also valuable for measuring adoption.
- Fine-Tune and Adjust: Use feedback and performance data to adjust the rules and thresholds for the AI agents.
After a successful pilot, the company can scale the automation to adjacent categories. This iterative process of piloting, monitoring, and scaling ensures the AI system evolves and continues to deliver value. It institutionalizes a learning loop where outcomes continuously improve the procurement process and advance sustainability goals.
Benefits and Challenges
Adopting autonomous procurement offers significant rewards but also presents notable challenges. Companies must weigh the transformative potential against the practical hurdles of implementation. A clear understanding of both sides prepares organizations for a successful transition.
Realizing Tangible Benefits
Autonomous systems deliver substantial financial and operational advantages. They optimize planning and inventory management, which reduces operational costs over time. The positive financial impact is clear and measurable.
| Benefit | Reported Improvement |
|---|---|
| Procurement Cost Savings | 20-30% |
| Supplier Contract Costs | 20% reduction |
| Negotiation Terms | 12-18% better |
| ESG Goal Achievement | 27% faster |
Beyond cost, these systems enhance brand reputation. AI agents enforce compliance by continuously monitoring supplier practices against ESG standards. They can detect violations in real time and flag non-compliant partners automatically. This proactive stewardship ensures that procurement decisions align with corporate values and regulatory requirements, strengthening stakeholder trust.
Overcoming Implementation Hurdles
Organizations face several hurdles when implementing autonomous systems. Data integration is a primary obstacle. A 2023 survey found that 62% of procurement professionals identify data integration as a significant challenge. Poor data quality and security risks can lead to hidden costs and system complexity.
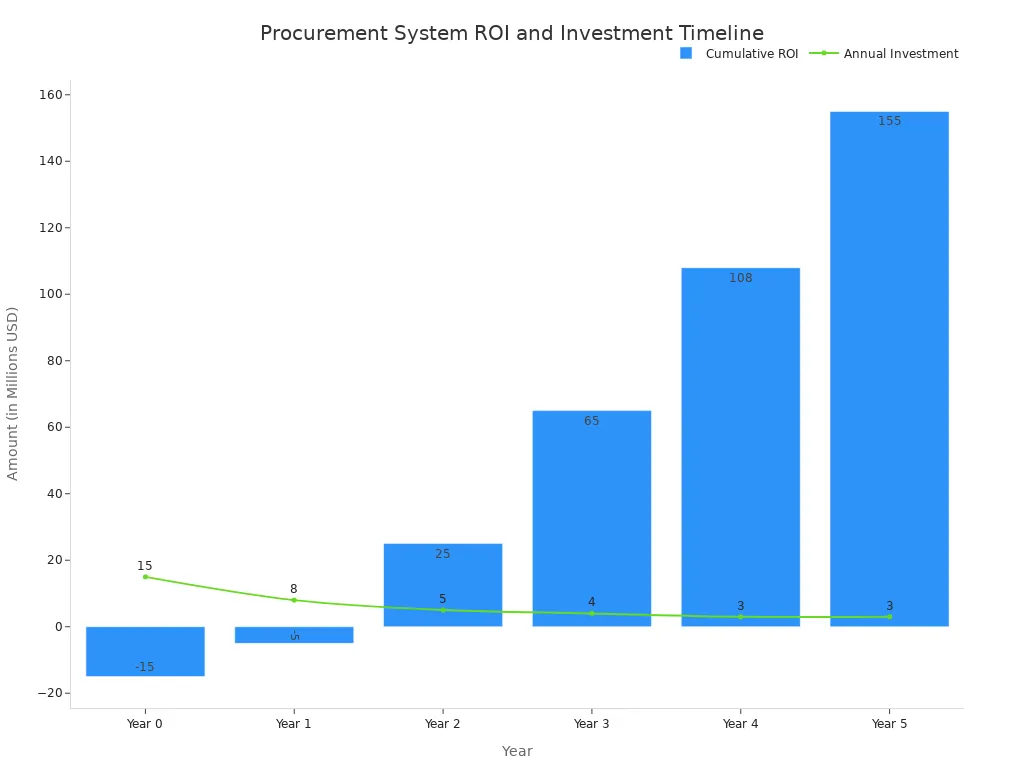
The initial investment is another key consideration. While substantial, the return on investment (ROI) materializes over a clear timeline. A large enterprise can expect a break-even point around month 18, with the net impact growing significantly in subsequent years.
Finally, companies must manage the human factor. Employee resistance often stems from a fear of complexity.
Strategy for Success: Overcome resistance by securing leadership buy-in and communicating the "why" behind the change. Pilot programs and tailored training help build user confidence and demonstrate direct benefits, turning apprehension into adoption.
Autonomous procurement planning is a practical tool for achieving real sustainability gains today, not a distant concept. Companies like Alcoa and EnBW already use these systems to meet measurable ESG targets. This technology transforms sustainability from an idea into a core business metric. Begin the journey toward a more resilient and responsible supply chain by defining clear goals for your procurement strategy.
FAQ
What is the main difference between autonomous and traditional procurement?
Autonomous systems use AI to make purchasing decisions with minimal human input. Traditional procurement relies on manual tasks and human intervention. This new model creates a proactive, data-driven function that operates continuously.
How does autonomous procurement improve sustainability?
AI agents automatically vet suppliers against a company's ESG goals. The system optimizes shipping routes to lower carbon emissions. It embeds sustainability rules directly into the purchasing process, ensuring compliance with every transaction.
Is this technology only for large corporations?
No, this technology is not just for large companies. Scalable platforms and cloud-based solutions make autonomous procurement accessible for mid-sized businesses. These systems can grow with a company's needs and budget.
What is the role of human teams with this system?
Human teams shift from manual tasks to strategic work. They focus on managing supplier relationships, setting ESG goals, and overseeing system performance. The AI handles routine execution, freeing up professionals for high-value initiatives.
See Also
Achieve Sustainable Supply Chains: Three Lean Logistics Strategies for Success
Secure Your B2B Order Fulfillment: Strategies for Enduring Success
Rapid, Sustainable Supply Chain Success Through Lean Logistics Principles
Enhancing Business Agility: The Role of Supply Chain Outsourcing Providers
Fueling Business Expansion: Leveraging Supply Chain Management Outsourcing