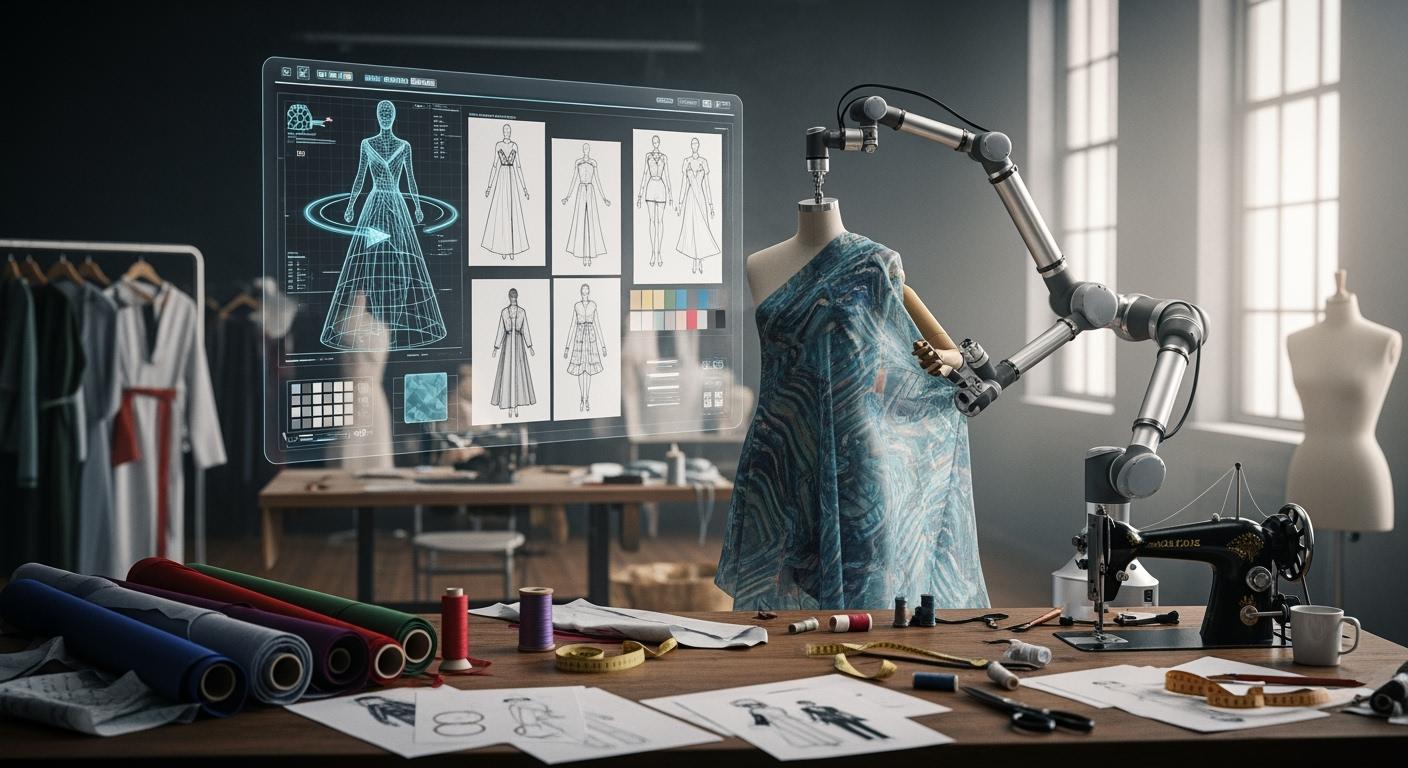

By 2025, the key impact of generative AI in fashion design extends beyond image creation. It now involves the realistic simulation of physical products. The fashion industry faces immense waste from physical sampling. Designers often create numerous prototypes for a single design.
- The footwear sector alone produces around 26 million physical samples annually.
- Shipping these samples contributes an estimated 397 billion tons of CO₂.
Generative AI in fashion tackles this problem head-on. AI tools allow designers to perfect a garment's fit and fabric drape digitally. This shift to digital-first fashion promotes sustainability. The growth of this market is clear.
| Metric | Projected Value by 2025 |
|---|---|
| Digital-first fashion market size | $2.94 billion |
| AR adoption in digital fashion | 33% increase |
This powerful AI enables a move toward sustainable fashion, where generative AI helps designers create better products with less waste.
The Rise of Digital-First Fashion

The fashion industry is moving toward a digital-first model. Generative AI is the engine driving this change. This technology allows designers to create, test, and perfect garments in a virtual space before a single piece of fabric is cut. This shift fundamentally changes the design workflow for fashion.
Creating Digital Twins to Cut Waste
Designers now use generative AI to build digital twins of their products. These are highly realistic digital prototypes. This process is a core part of the new approach to fashion. The AI can simulate how a garment will look and perform, which improves product quality. Major brands already see the benefits. Adidas uses this AI to test footwear performance. Levi's employs it to perfect the fit and quality of its jeans, even showing how they look after many washes. This focus on digital creation has a huge impact on sustainability.
Some brands have seen an 80% reduction in physical samples by using AI. This technology helps designers create better fashion with far less waste. The use of AI also allows for greater product customization.
Accelerating Sample Approval
The traditional sample approval process is a major bottleneck. Physical samples can take weeks or months to create and ship. Generative AI transforms this timeline. Digital simulations reduce design approval time from weeks to mere hours. This speed offers several advantages:
- Designers receive feedback almost instantly.
- Developers avoid unnecessary rework.
- Merchandisers can plan their collections earlier.
This AI-powered workflow allows designers to make changes and see the results immediately. A designer can adjust a seam, change a color, or test a virtual try-on in minutes. This rapid iteration was impossible with physical samples.
Enhancing Creative Freedom
Generative AI in fashion also unleashes creative potential. Designers are no longer limited by the cost and time of physical prototyping. They can explore bold ai-generated designs without risk. The AI allows them to experiment with any digital textile or pattern. This freedom is one of the most exciting use cases of generative ai. Designers can test dozens of variations for a single design. They can see how a complex garment fits on different body types using virtual try-on technology. This powerful AI gives designers the tools to push the boundaries of fashion and innovate faster than ever before. Generative AI in fashion is making the entire design process more dynamic.
Core Application of Generative AI
The core applications of generative AI in fashion design are transforming how designers bring ideas to life. This technology moves beyond simple image creation. It now provides tools for realistic simulation and rapid prototyping. These applications are the engine behind a more efficient and sustainable fashion industry.
How AI Simulates Fabric Behavior
Generative AI excels at simulating how different fabrics behave in the real world. This material simulation is a critical use case of generative ai. The AI analyzes material science data, including fiber type, yarn structure, and weave density. It then uses advanced physics engines to model complex behaviors like drape, stretch, and folding with high accuracy. The AI learns from vast datasets of real-world materials to generate convincing digital replicas. This process allows it to show the fluid motion of chiffon or the structured form of denim.
To achieve this realism, the AI uses specific data points to simulate textile behavior.
- Stiffness: The AI analyzes yarn paths and weave architecture to predict a fabric's bending stiffness.
- Stretch: It uses data on tensile elongation and stretch force to model how much a fabric will give.
- Weight: The system considers the fabric's weight to determine how it hangs and drapes on a form.
This detailed approach ensures that the virtual garment behaves just like a physical one, giving designers reliable feedback on their design choices.
Accurate Fit on Diverse Body Avatars
Generative AI provides tools to ensure garments fit a wide range of body types. Designers use AI to create high-resolution 3D body models, or avatars, from simple smartphone scans or measurements. This technology helps the fashion industry become more inclusive. Brands like Bold Metrics and True Fit use AI to generate precise body measurements for better size guides.
The AI aligns a customer's body measurements with a product's specific dimensions. It also considers fabric elasticity, which greatly affects fit. This allows for better customization. The system can even integrate a customer's personal wear preferences. For example, a designer can use virtual try-on technology to see how a dress fits on dozens of different virtual body shapes. This AI-powered try-on process helps designers create clothing that fits beautifully on everyone, improving product quality and customer satisfaction.
From 2D Pattern to 3D Garment
One of the most powerful applications of generative AI is converting a 2D design pattern into a realistic 3D garment. This complex process involves several key steps.
- First, the AI encodes the 2D sewing pattern and 3D draping information into a special format.
- Next, a powerful AI model learns from this data to generate a complete garment model from the raw 2D pattern.
- A specialized module then recovers the sewing relationships, turning the AI's output into a usable digital pattern and mesh.
- Finally, this digital pattern is ready for a physics-based simulation, which creates the final, realistically draped 3D garment.
This workflow allows designers to visualize their ideas in 3D almost instantly. It bridges the gap between a flat design sketch and a wearable product. This is a core part of textile design innovation, allowing for new types of pattern and print generation and complex prints to be tested quickly.
The Impact on Speed-to-Market
The use of generative AI in fashion dramatically accelerates the time it takes to bring a collection to market. Traditional sampling takes weeks or months. AI-driven digital sampling reduces this timeline to hours or days. This speed gives fashion brands a significant competitive edge. Designers can create and refine digital prototypes quickly, getting faster feedback and making immediate adjustments.
This efficiency has a measurable impact. For instance, one New York accessories boutique integrated machine learning to track shopping behavior. This allowed the brand to achieve a 52% faster collection development cycle. By using generative AI, fashion companies can respond more quickly to trends, reduce rework, and plan their collections with greater confidence. This rapid iteration, a key feature of generative AI in fashion design, ensures that new styles reach customers faster than ever before, improving both quality and relevance.
The AI Toolkit for Modern Fashion
Designers now use a powerful set of AI tools to bring their fashion ideas to life. This toolkit combines creative software with advanced simulation technology. The integration of these systems is what makes modern digital fashion possible.
Design and Simulation Suites
Leading 3D design suites are central to the digital fashion workflow. Platforms like CLO 3D and Browzwear allow designers to create true-to-life virtual garments.
- CLO 3D uses advanced simulation to visualize how a garment will drape and fit.
- Browzwear creates a "digital twin" of the product. This allows designers to validate the style and fit with high precision.
These tools help designers ensure the first physical sample can be the final one. This focus on digital accuracy improves the overall quality of the final product.
AI-Driven Design Platforms
Specialized AI-driven platforms offer unique capabilities for fashion. These platforms use generative AI to accelerate the creative process. For example, Raspberry AI helps designers generate new clothing ideas from simple text inputs. It also provides on-body visualization for virtual try-on. This allows teams to see how a design looks on a model without a physical photoshoot. This type of generative AI gives designers a powerful brainstorming partner, speeding up the entire design cycle.
Note: These AI platforms are different from standard 3D software. They focus on rapid ideation and concept generation, while 3D suites handle the technical construction and simulation.
Underlying Physics Engines
The realism of digital fashion depends on powerful underlying technology. AI physics engines, such as those used in NVIDIA Omniverse, are essential for reproducing textile properties. This AI technology simulates how cloth moves, folds, and interacts with a body. The AI models are trained on vast datasets to understand material characteristics. This ensures that a virtual silk dress moves differently than a denim jacket. This core AI capability is what gives digital prototypes their lifelike quality.
Data Input and Analysis Tools
High-quality data is crucial for effective generative AI in fashion. The AI relies on specific input tools to create accurate simulations. 3D body scanners capture precise measurements to create digital avatars for virtual try-on and better customization. Digital fabric analyzers provide the AI with data on material weight, stiffness, and stretch. This information feeds the generative AI models, enabling them to produce realistic results. Better data helps designers create fashion that fits perfectly and behaves as expected.
Navigating Challenges for Generative AI in Fashion
Generative AI offers incredible opportunities for the fashion industry. However, brands must navigate several key challenges to adopt this technology successfully. These hurdles range from financial costs to complex legal questions.
High Cost of Implementation
High initial costs for AI solutions present a major barrier. Many fashion brands, especially smaller ones, find the investment difficult. A U.S. Chamber of Commerce survey showed nearly 60% of small businesses see cost as an obstacle to new technology. The uncertain return on investment from AI also causes hesitation. This makes it hard for some companies to commit resources to generative AI tools.
Bridging the Industry Skills Gap
The fashion industry faces a significant digital skills gap. Designers and other professionals need new skills to use generative AI effectively. Leaders must cultivate a workplace culture that supports learning these next-generation tools. Bridging this gap requires a combined effort.
- Companies can offer internal upskilling and practical workshops.
- Educators must innovate teaching methods to prepare students.
- Partnerships between industry, academia, and tech providers are crucial.
This training helps designers adapt their practices for long-term success with AI.
Data Bias and Ethical Concerns
Data bias is a serious ethical issue for generative AI in fashion. AI models trained on limited data can create problems with product quality and inclusivity.
If AI is trained on limited or skewed data—say, primarily on slim, white, able-bodied models—it can perpetuate harmful stereotypes and exclude diverse body types. Ensuring inclusivity and fairness in AI recommendations is an ongoing challenge that the industry must confront head-on.
Brands must ensure their AI tools use diverse datasets to produce fair and inclusive results. This focus on data quality is essential for ethical AI.
Intellectual Property Questions
Ownership of AI-generated design work creates complex legal questions. Current laws, such as in the U.S., generally require human authorship for copyright protection. A design created solely by AI may not be protectable. The case Thaler v. Perlmutter confirmed that only humans can be authors. There is no clear international agreement on who owns AI-assisted fashion creations. Designers should carefully document their creative input when using generative AI. This helps establish their role in the design process and protect their intellectual property.
By 2025, generative ai for simulation is the critical link in fashion. This AI connects creative design with viable production and sustainability. The future of fashion is a collaborative partnership. Designers guide generative ai tools. Designers use this AI to test and perfect garments with virtual methods. Designers create digital prototypes with this powerful AI. Generative ai in fashion helps designers. This AI makes fashion better. The AI is essential for modern fashion.
Brands that fail to adopt this AI and virtual technology will face significant competitive disadvantages. This generative ai is key for the fashion industry. The AI is a must for success.
FAQ
How does generative AI improve sustainability in fashion?
Generative AI reduces physical waste. Designers create and test digital prototypes first. This process significantly cuts down the number of physical samples needed for production. It also lowers the carbon footprint from shipping samples, making the industry more sustainable.
Is generative AI replacing fashion designers?
No, AI is a tool that assists designers. It enhances their creativity and efficiency.
- Designers guide the AI to generate ideas.
- They use AI simulations to test fit and drape.
- The technology handles repetitive tasks, freeing designers for creative work.
What skills do designers need to use AI tools?
Designers need a blend of creative and technical skills. They must learn to operate 3D design software like CLO 3D. Understanding data input for fabric simulation is also important. This combination of skills helps them use AI effectively in their workflow.
Can small fashion brands use generative AI?
Yes, adoption is becoming more accessible. While high-end systems are expensive, many platforms now offer subscription-based models. These options lower the entry cost, allowing smaller brands to leverage AI for design, simulation, and faster speed-to-market.
See Also
AI-Powered Fashion Innovations: Crafting a Sustainable Future for Our Planet
Navigating Viral Trends: AI's Role in Rapid Fashion Adaptation
Machine Learning: Predicting Fashion Trends to Significantly Boost Retail Sales
Transformative Impact of AI Sensors on the 2025 Fashion Supply Chain
Leveraging Predictive Models for Future Success in 2025 Fashion Retail