
AI systems coordinate complex multi-country supply hubs. They use technologies like agentic AI, reinforcement learning, and digital twins. These platforms automate decision-making and optimize logistics with real-time data. This digital transformation is fueling significant investment in the sector.
The AI in logistics market is projected to reach US$306.76 billion by 2032, reflecting its growing importance.
Ultimately, these ai systems help organizations proactively manage cross-border risks, building more resilient global operations.
Core AI Technologies for Hub Coordination

Modern ai systems use several key technologies to manage multi-country hubs. These tools process vast amounts of information. They enable organizations to make faster, smarter decisions across their global networks.
Agentic AI and Multi-Agent Systems
Agentic AI uses a Large Language Model (LLM) as a central brain. This LLM coordinates specialized AI "agents" that handle specific tasks. These multi-agent systems create powerful autonomous systems for supply chain management.
- Logistics agents optimize delivery routes and warehouse operations.
- Risk agents monitor global events and trigger backup plans automatically.
- Production agents adjust manufacturing schedules to meet changing demand.
These agents work together to execute complex plans without human intervention. For example, if a port closes, agents can detect the disruption, calculate new routes, and shift orders to alternative suppliers.
Reinforcement Learning for Route Optimization
Reinforcement Learning (RL) helps ai systems find the best possible shipping routes. RL models learn through trial and error. They constantly adapt to real-time data on traffic, weather, and fuel prices.
UPS uses its ORION system, an RL-based platform, to optimize delivery routes. This system saves the company over $400 million annually in fuel and operational costs.
Algorithms like Deep Deterministic Policy Gradient (DDPG) are particularly effective. They can reduce ship fuel consumption by over 6% by continuously refining route choices. This technology makes logistics more efficient and sustainable.
Digital Twins for Network Visibility
A digital twin is a virtual replica of a physical supply chain. It integrates data from many sources, including:
- GPS data from trucks
- Warehouse sensor feeds
- ERP and order management systems
- Partner updates
This complete digital model provides total supply chain visibility. Companies like DHL use digital twins to simulate network changes, test new workflows, and optimize warehouse layouts before making physical changes. This allows managers to identify bottlenecks and improve processes with minimal risk.
Key Applications of AI
AI technologies offer powerful applications for global supply chain management. They process massive datasets to find patterns, predict problems, and give clear instructions. These applications transform how organizations manage their operations across multiple countries.
Autonomous Demand Forecasting
Accurate demand forecasting is critical for efficient supply chain operations. AI models analyze historical sales, market trends, weather patterns, and economic indicators. This analysis helps companies predict future customer demand with greater precision. AI-driven demand forecasting routinely improves accuracy by over 20% compared to traditional methods. This leads to better inventory optimization and reduced waste.
A McKinsey study found that companies using advanced analytics can improve forecasting accuracy by up to 50%. For example, an apparel maker achieved 95% forecast accuracy after implementing an AI tool.
These improvements allow businesses to align their stock levels with actual demand. Better demand forecasting directly supports superior inventory optimization. The table below shows how different AI tools improve forecast accuracy.
| Tool | Forecast Accuracy Improvement |
|---|---|
| Blue Yonder | Up to 35% |
| o9 Solutions | ~15% |
| ToolsGroup | Up to 35% |
| NetSuite Forecast | ~50% visibility improvement |
| GMDH Streamline | Up to 95% accuracy |
AI in Global Logistics Management
AI streamlines global logistics management by automating complex processes. It enhances tracking, communication, and compliance across borders. AI systems process customs documents, classify goods with correct tariff codes, and ensure all paperwork is complete before submission. This automation significantly reduces delays and prevents costly fines.
AI automates customs clearance through several key steps:
- Document Extraction: AI uses Optical Character Recognition (OCR) and Natural Language Processing (NLP) to pull data from invoices, packing lists, and bills of lading.
- Automated Cross-Verification: The system checks documents for consistency in product details, quantities, and destination information.
- Live Regulation Mapping: AI monitors global trade rules and flags shipments that may violate current restrictions or require special licenses.
- Compliance Checklist Generation: The system creates a checklist for each shipment, highlighting missing information or potential issues.
This level of automation provides complete supply chain visibility. It connects information from different partners into one unified workflow. This helps organizations manage shipments more effectively from origin to destination.
Proactive Risk Mitigation
Modern supply chains face constant threats from weather, geopolitical events, and supplier issues. AI systems analyze diverse datasets to predict these disruptions before they happen. They process historical shipment records, real-time data from sensors, news feeds, and social media to identify potential risks.
These platforms provide actionable alerts that allow managers to respond proactively. For example, an AI tool can detect a potential port strike and recommend rerouting shipments through an alternative hub. This capability turns risk management from a reactive process into a proactive strategy. Many companies have achieved significant results using these tools.
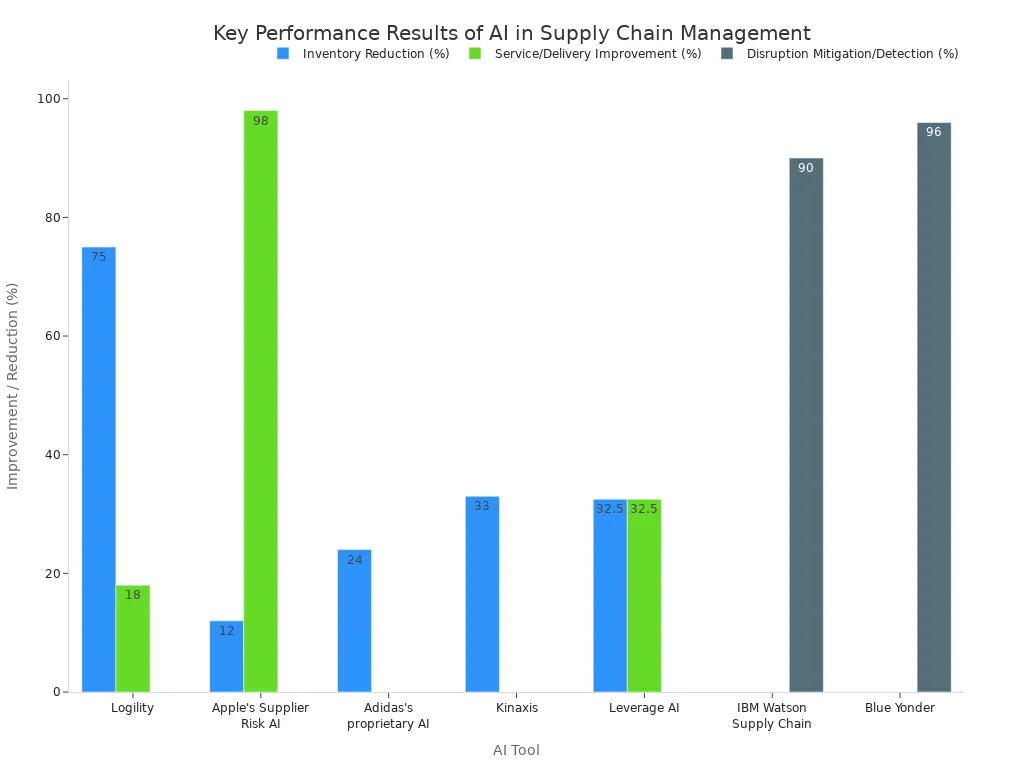
This proactive approach builds resilience. It empowers organizations to navigate global uncertainties with confidence and maintain operational continuity.
Quantifiable Benefits of AI Integration
Integrating AI into multi-country hubs delivers significant, measurable advantages. These systems move beyond simple automation. They create intelligent, responsive networks that enhance performance and reduce costs. The benefits range from improved agility in the face of disruption to the creation of fully autonomous supply chains.
Enhanced Agility and Resilience
AI enhances supply chain resilience across three core dimensions. It reduces dependence on single suppliers, strengthens operational continuity, and improves overall efficiency. AI-driven supply chains can anticipate disruptions and adapt in real-time. This capability allows organizations to navigate uncertainty with confidence.
Several companies have demonstrated this agility during major global events:
- Unilever avoided $19 million in losses. Its AI system detected negative trends in labor negotiations and rerouted shipments 10 days before a port strike began.
- Coca-Cola's European division maintained 96% fulfillment rates during transport chaos. The company used AI to balance customs rules, demand shifts, and carbon targets, adjusting production within hours of rail strikes.
- A furniture brand rerouted shipments via air freight during the Suez Canal blockage. This decision, informed by live port congestion analytics, helped it avoid $3 million in delays and recover 40% faster than competitors.
AI improves key metrics that measure resilience. It provides greater visibility and control over the entire network.
| Metric | How AI Improves It |
|---|---|
| Forecast accuracy | Enhanced precision |
| Order-to-delivery lead time | Faster deliveries |
| Inventory-to-sales ratio | Reduced holding costs, more precise replenishment |
| Total supply-chain cost | 10-20% fuel savings via route optimization, lower waste |
Reduced Operational Costs
AI directly lowers operational costs across the supply chain. Early adopters have seen logistics costs drop by an average of 15%. These savings come from smarter resource allocation, waste reduction, and process automation.
One of the biggest areas of savings is inventory optimization. AI models analyze historical data, market trends, and real-time signals to create highly accurate demand forecasts. This precision helps businesses reduce stockouts by up to 30%. It also cuts excess inventory by 20-35%, which lowers warehouse holding costs and improves cash flow. Smart replenishment systems use AI to dynamically adjust reorder points. This ensures product availability without creating wasteful overstock.
Fuel savings are another significant benefit. Route optimization algorithms analyze traffic, weather, and sea conditions to find the most efficient paths.
UPS saves 10 million gallons of fuel annually with its AI-powered ORION system.
This technology reduces fuel consumption for land, sea, and air freight. It makes logistics more cost-effective and sustainable. The ai systems also optimize energy usage on ships and in warehouses for additional savings.
Building Autonomous Supply Chains
The ultimate goal of AI integration is to build autonomous supply chains. These advanced networks manage and optimize themselves with minimal human intervention. They rely on a strong digital core that unifies data from every part of the supply chain. This creates a single, accessible platform for real-time decision-making.
Autonomous supply chains have several key characteristics:
- Predictive: They monitor data to anticipate errors, bottlenecks, and inefficiencies before they occur.
- Intelligent: They use AI and machine learning to process data, identify trends, and make dynamic decisions.
- Scalable: They automatically adjust operations up or down to meet changing demand and optimize resource use.
- Integrated: They connect all logistics operations into a single, synchronized workflow, enabling complete product traceability.
Building autonomous supply chains requires an agentic architecture where AI agents handle specific tasks. This structure supports self-sustaining and adaptive operations. In this model, human roles shift from manual execution to strategic oversight and system management. These autonomous systems can plan in real-time and execute operational actions frequently and cost-effectively. This evolution creates a truly integrated digital supply chain that is both resilient and highly efficient, paving the way for the future of global logistics. The development of autonomous supply chains represents the next frontier in operational excellence.
Challenges in Implementing AI Systems

Adopting AI for multi-country hubs presents significant challenges. Organizations must navigate technical hurdles, complex regulations, and resource limitations. Overcoming these obstacles is crucial for a successful digital transformation.
Data Integration and Standardization
Effective AI relies on high-quality, unified data. However, many companies struggle with data integration. Legacy systems like ERPs and WMS often use different data formats, which complicates data flow and synchronization. These older platforms were not built for the real-time demands of modern AI.
To solve this, organizations must establish clear data governance policies. Best practices for data integration include:
- Standardizing Data: Define consistent naming conventions, units, and formats across all systems.
- Harmonizing Sources: Align data from multiple internal and external sources for AI processing.
- Implementing Governance: Assign data owners to monitor quality and maintain data lineage for traceability.
Proper data integration ensures that AI models receive reliable information to generate meaningful insights.
Regulatory and Sovereignty Issues
Global operations require compliance with various data sovereignty laws. These regulations control how companies can share data across borders. The rules differ significantly by region, creating a complex legal landscape. For example, China's laws focus on national security, while the EU's GDPR prioritizes individual rights.
| Law/Region | Key Focus | Cross-Border Transfer Restrictions |
|---|---|---|
| China (CSL, PIPL) | National security, data security | Strict regulations, emphasizes user consent |
| GDPR (EU) | Protecting EU citizens' personal data | Restrictions to ensure adequate protection outside EU |
These differing legal frameworks complicate global AI governance. Companies must carefully manage data flows to avoid penalties and ensure compliance in every market.
Investment and Talent Scarcity
Implementing advanced AI requires significant financial investment and specialized expertise. The logistics sector faces a severe talent shortage. Demand for data scientists and machine learning engineers far exceeds the available supply. Companies find it difficult to attract and retain professionals with the right skills. This talent crunch slows the pace of innovation, as organizations struggle to find the personnel needed to build and manage sophisticated AI solutions.
AI transforms multi-country supply chains into resilient, autonomous networks. Success depends on choosing the right technologies for specific applications. For example, companies can use agentic AI for risk mitigation or digital twins for logistics optimization. Organizations that overcome data integration and regulatory challenges will unlock significant cost savings. They will also gain a major competitive advantage in the global marketplace. These autonomous systems represent the future of efficient global trade.
FAQ
What is the main role of AI in a multi-country hub?
AI systems automate complex decisions for global hubs. They optimize logistics, forecast demand, and manage cross-border risks. This technology helps organizations build more efficient and responsive supply networks that operate across multiple countries.
How does AI help reduce supply chain costs?
AI directly lowers operational expenses. It optimizes shipping routes to save fuel and improves demand forecasting to reduce inventory holding costs. Automation of routine tasks, like customs paperwork, also cuts administrative expenses and prevents costly fines.
What is an autonomous supply chain?
An autonomous supply chain uses AI to manage itself with minimal human intervention. It predicts disruptions, makes intelligent decisions, and scales operations automatically. This creates a highly efficient and resilient network that adapts to change in real-time.
Why is data integration a major challenge?
Many companies use older systems with different data formats. AI requires clean, standardized data to work correctly. Integrating and harmonizing information from various sources is a complex but essential first step for successful AI implementation.
See Also
Do Your AI Systems Analyze Social Media Conversations and Trends?
Predicting Future Demand Using AI and Data Analytics by 2025
AI Algorithms Significantly Reduce Fashion Delivery Times by Over One-Fifth
Dynamic Safety Stock AI: A 2025 Solution for Fashion Retailers
Transforming Warehouse Operations: The Power of Dynamic Slotting Strategies