
Warehouse audits play a vital role in identifying inefficiencies, reducing waste, and ensuring compliance in warehouse operations. These assessments uncover hidden mistakes, improve inventory management, and help teams follow safety protocols. Regular warehouse audit processes enhance productivity, optimize space usage, and reduce accidents. Audits also provide a structured approach to diagnose root causes and support data-driven decisions. By focusing on measurable results, warehouse audit practices drive operational efficiency and continuous improvement across every part of the facility.
Warehouse Audits Overview

What Is a Warehouse Audit
A warehouse audit is a comprehensive review of all warehouse operations. This process helps leaders find areas for improvement and supports compliance with industry standards. During a warehouse audit, teams observe daily activities, check staff training, and measure key metrics. They also look at how well equipment and technology work. The goal is to make sure the warehouse runs safely, efficiently, and meets industry benchmarks.
A warehouse audit gives companies a clear picture of their strengths and weaknesses. It helps them compare their performance to best practices and find ways to save money or reduce errors.
The table below summarizes how industry standards define a warehouse audit and its main functions:
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Definition | A warehouse audit is a comprehensive, high-level assessment of all warehouse operations and functions aimed at identifying specific opportunities for improvement. |
| Primary Functions | Evaluating safety, facility cleanliness, standardization and measurability of operations, equipment and technology utilization, continuous improvement, waste reduction, receipt and order entry methods, inventory validation, and staff training. |
| Purpose | To enable leadership to analyze operations efficiently, identify cost savings, reduce errors, benchmark against best practices, and foster continuous improvement. |
| Audit Activities | Observing processes, assessing staff performance and training, measuring key metrics, ensuring standardized procedures are consistently followed. |
| Outcome | Ensures the warehouse runs safely, efficiently, and competitively within industry standards. |
Audit Objectives
Warehouse audits have several main objectives. These goals guide the warehouse operations assessment and help companies achieve better results. According to logistics associations, the main objectives include:
- Enhancing efficiency by finding and removing redundant steps in workflows.
- Reducing costs by identifying unnecessary spending and suggesting better options.
- Ensuring compliance with laws and industry rules.
- Mitigating risks by spotting challenges early and planning solutions.
- Improving customer satisfaction through faster deliveries and fewer mistakes.
- Assessing technology to make sure software and automation tools meet company needs.
Warehouse audits support continuous improvement. They help teams keep up with changes in the industry and maintain high standards. By focusing on these objectives, companies can use warehouse audits as a strategic tool for ongoing success.
Key Audit Areas
Inventory Accuracy
Warehouse audit teams focus first on inventory accuracy. Accurate inventory records help companies avoid overstocking and stockouts. Regular counting and tracking improve order fulfillment rates and reduce operational costs.
- Frequent inventory checks can increase sales by up to 8%.
- Accurate data ensures products are available for customers, which leads to higher satisfaction.
- Companies with high inventory accuracy spend less on inventory costs and avoid wasted time searching for misplaced items.
- Errors in inventory can cost businesses millions each year and cause lost sales or damaged customer relationships.
Accurate inventory supports better demand forecasting and production planning, which strengthens operational efficiency and cash flow.
Process and Workflow
Warehouse audit teams review process and workflow to identify bottlenecks and inefficiencies. Audits help ensure items are in the right place, which speeds up order fulfillment.
- Regular process reviews and employee feedback highlight areas for improvement.
- Technology like barcode scanners and warehouse management systems (WMS) reduces human error and provides real-time data.
- Monitoring key performance indicators, such as order accuracy, helps teams make better decisions and improve efficiency.
A well-designed workflow reduces wasted time and supports continuous improvement in warehouse operations.
Warehouse Safety Audits
Warehouse safety audits protect employee well-being and reduce workplace accidents.
- Hazard communication, including proper signage and training, remains a top concern.
- Respiratory protection programs and safe ladder use are common issues.
- Forklift operation and maintenance require regular checks.
- Electrical wiring, scaffolding, and guardrails must meet safety standards.
- Ongoing safety training and clear labeling prevent accidents.
Warehouse safety audits ensure compliance with regulations and create a safer work environment.
Technology and Systems
Warehouse audit teams assess technology and systems to support operational efficiency.
- A WMS improves data accuracy and workflow integration.
- Regular audits and employee training keep systems reliable.
- Continuous monitoring of performance metrics helps maintain high standards.
- Effective technology use streamlines warehouse operations and supports accurate audits.
Technology-enabled audits provide real-time insights and help teams respond quickly to changes.
Layout and Space Use
Warehouse audit teams evaluate layout and available space utilization to maximize efficiency.
- Assessments identify bottlenecks and improve product placement.
- Using vertical space, optimizing slotting, and reducing aisle widths increase storage capacity.
- Flexible layouts and clear pathways support safety and future growth.
- WMS and automation help optimize available space utilization and improve operational assessment.
A well-planned layout reduces travel time, improves workflow, and lowers the risk of workplace accidents.
Audit Process Steps
Planning
A successful warehouse audit begins with careful planning. The audit process starts by analyzing current workflows, facility layout, and labor efficiency. Teams gather data from reports and review key performance indicators. They conduct a SWOT analysis to find strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. Interviews with employees help reveal pain points that affect daily operations. The team lists these issues and rates them by severity. This step ensures the warehouse audit focuses on the most critical areas, such as safety and customer satisfaction. Planning also includes setting clear goals and tracking progress over time.
On-Site Review
During the on-site review, auditors walk through the warehouse and observe daily activities. They use detailed checklists and digital tools to record findings. The table below shows key areas reviewed during this phase:
| Category | Checklist Points |
|---|---|
| Safety and Security | Emergency exits, safety gear, fire extinguishers |
| Organization | Clear aisles, labeled shelves, clean workspaces |
| Inventory Management | Accurate counts, proper labeling, damaged goods |
| Equipment | Maintenance logs, operator training, safety checks |
| Compliance | Up-to-date permits, regulation adherence |
| Documentation | Shipping records, safety inspections, inventory logs |
| Training | Employee safety training, new procedure sessions |
Auditors also check equipment, review training records, and confirm compliance with safety rules. They note both quick fixes and larger projects for future action.
Data Analysis
After the on-site review, the audit process moves to data analysis. Teams use warehouse management systems and analytics tools to study the collected data. They look for trends, such as repeated inventory errors or delays in order fulfillment. Predictive analytics help spot potential stock problems before they grow. Automation tools and smart sensors provide real-time updates on product location and condition. By comparing planned and actual labor hours, teams can find hidden costs and inefficiencies. This step turns raw data from the warehouse audit into clear, actionable insights.
Reporting
The next step in the audit process is reporting. Auditors prepare a detailed report that covers all findings. The report includes ratings for each area, highlights pain points, and offers specific recommendations. It also sets timelines for making improvements. Managers, supervisors, and staff review the report together to ensure everyone understands the results. Regular audits and clear reports help keep the warehouse audit process transparent and effective.
Improvements
The final step is implementing improvements. Teams create action plans with assigned responsibilities and deadlines. They use technology to monitor progress and track changes. Leaders encourage staff to view audit findings as opportunities for growth. Regular follow-ups and dashboards help measure the impact of changes. By repeating the warehouse audit regularly, companies build a culture of continuous improvement and accountability.
Tip: Continuous monitoring and regular audits ensure that improvements last and the warehouse stays efficient and safe.
Enhancing Operational Efficiency

Warehouse audits deliver measurable improvements across cost, speed, space, and safety. By focusing on enhancing operational efficiency, companies can unlock significant value in their supply chains. The following sections highlight how audits drive cost reduction, throughput gains, space optimization, and compliance.
Cost Reduction
Warehouse audits help organizations reduce operational costs by identifying inefficiencies and eliminating waste. Teams often discover hidden expenses in labor, storage, and shipping. For example:
- A mid-sized electronics distributor improved picking speed by 30% after redesigning the layout and adding barcode scanning. This change reduced mis-picks and increased customer satisfaction.
- A retail distribution center cut picker travel distance by up to 70%, decreasing aisle visits by 60%. This adjustment significantly increased processing capacity.
- A food distributor reduced receiving times by 40% by requiring advanced shipping notices with pallet-level details.
- Automation initiatives lowered labor requirements by up to 30%, improving safety and reducing costs.
Warehouse audits also reveal the true cost of different distribution strategies. The table below compares annual costs for a single warehouse versus two regional warehouses:
| Cost Factor | Single Warehouse (Central U.S.) | Two Warehouses (East + West Coast) |
|---|---|---|
| Shipping Costs | $70,000 | $63,000 (10% savings) |
| Warehouse Storage | $30,000 | $40,000 (duplicated facilities) |
| Inbound Freight | $20,000 | $35,000 (shipping to 2 locations) |
| Inventory Carrying | $10,000 | $15,000 (extra stock) |
| Labor & Operations | $25,000 | $40,000 (two teams) |
| Systems & Technology | $5,000 | $8,000 (upgraded systems) |
| Total Annual Cost | $160,000 | $201,000 |
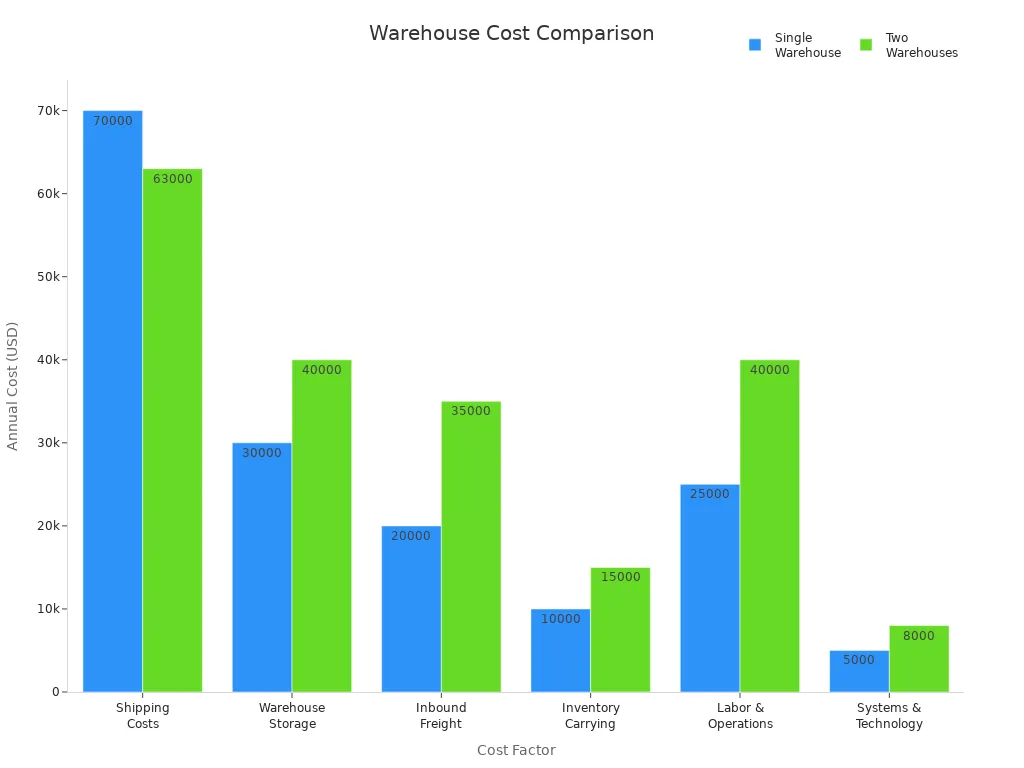
This analysis shows that while two warehouses may save on shipping, they incur higher costs in other areas. Warehouse audits help leaders make informed decisions to optimize cost savings.
Throughput Gains
Warehouse audits play a key role in improving performance metrics and increasing throughput. Teams use audits to identify bottlenecks, reduce errors, and streamline workflows. Some proven strategies include:
- Organizing inventory by re-evaluating layout, labeling, and grouping items.
- Implementing ongoing cycle counts to maintain inventory accuracy and ensure timely replenishment.
- Scheduling simultaneous shipments to reduce loading and unloading time.
- Minimizing unnecessary handling steps to make processes faster and leaner.
Key metrics for measuring throughput gains include warehouse throughput, truck time at the dock, time from receiving to pick location, receiving efficiency, labor productivity, space utilization, and overall equipment effectiveness. By tracking these metrics, managers can quantify improvements and sustain higher operational efficiency.
Regular audits and continuous improvement plans ensure that throughput gains are not just temporary but become part of the warehouse’s standard operations.
Space Optimization
Enhancing operational efficiency also depends on effective space utilization. Warehouse audits uncover hidden storage opportunities and help teams maximize every square foot. Effective strategies include:
- Conducting thorough space audits to identify underused areas.
- Using technology such as drones or 3D mapping tools for detailed layout analysis.
- Installing mezzanines and vertical shelving to optimize vertical space.
- Utilizing overlooked areas like corners and spaces above offices.
- Employing mobile racking systems and multi-purpose furniture for flexible storage.
Regular audits ensure that inventory levels remain accurate, reducing both stockouts and overstocking. This approach leads to cost savings and better space management.
A well-organized warehouse layout reduces travel time, improves workflow, and lowers the risk of workplace accidents.
Compliance and Safety
Warehouse safety audits are essential for maintaining compliance and reducing workplace accidents. Audits address key requirements such as:
- Properly marked and unobstructed emergency exits.
- Secure and stable racking systems.
- Valid forklift operator certifications and up-to-date training records.
- Written hazard communication programs, including labeling and safety data sheets.
- Maintenance of injury and illness logs.
Warehouse safety audits also evaluate storage practices, equipment maintenance, and employee training. By identifying hazards and implementing corrective actions, audits foster a safer work environment and ensure compliance with OSHA, FDA, and environmental regulations.
| Benefit | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Safeguarding Employee Well-being | Audits identify and mitigate risks from machinery, hazardous materials, and storage systems. |
| Reducing Workplace Accidents | Proactive hazard identification and corrective measures reduce accident likelihood. |
| Compliance with Legal Standards | Audits ensure adherence to safety regulations, avoiding penalties and operational disruptions. |
| Enhancing Operational Efficiency | Optimizing safety protocols and traffic flow reduces downtime and improves productivity. |
| Fostering a Culture of Safety | Regular reviews and training engage employees, increasing safety awareness and ownership. |
| Continuous Improvement | Ongoing audits track performance, identify trends, and support protocol updates for better safety. |
Warehouse audits not only protect employees but also support operational efficiency by minimizing disruptions and promoting a culture of safety.
Effective Warehouse Audits
Audit Checklist
A comprehensive warehouse audit checklist helps teams maintain safe and efficient operations. This tool covers critical areas such as safety, storage, inventory, loading, housekeeping, and maintenance. Using a checklist improves quality control, equipment uptime, and cost savings. It also helps identify hazards like forklift accidents or slips and falls. A typical checklist includes:
- Emergency exits are clear and easy to access.
- Fire doors open from the inside without obstruction.
- Power leads and outlets are undamaged and safe.
- Aisles and floors remain free of clutter and trip hazards.
- Lighting works well and is not blocked.
- Loading dock doors and access points are in good condition.
- Workbenches are clean and stable.
- Equipment is organized and operational.
- Pallets and racks are stable and undamaged.
- Chemicals are stored safely and labeled.
- First aid cabinets are stocked and clean.
- Floors are free from spills or ice.
- Walls and barriers are intact.
- No gas or water leaks are present.
- Air quality meets safety standards.
Regular use of a warehouse audit checklist supports operational efficiency and keeps staff safe.
Using Technology
Modern technology transforms the warehouse audit process. Barcode scanners and RFID systems automate inventory counts, saving time and reducing labor. RFID can scan multiple items at once, which increases speed and accuracy. Real-time inventory visibility allows teams to spot low stock and act quickly. Automated data entry reduces human error and improves order accuracy. Warehouse management systems (WMS) integrate with these tools to provide instant updates on stock levels and movement. This technology also maintains detailed audit trails, supporting compliance and making audits faster and more reliable.
Continuous Improvement
Continual process improvement stands at the heart of effective warehouse audit practices. Regular audits help teams find new ways to enhance workflows and boost efficiency. Key principles include accuracy, compliance, risk management, and clear communication. Teams track performance using KPIs like inventory turnover, order accuracy, and labor productivity. They use audit feedback to refine processes and train staff. A culture of continual process improvement encourages employees to suggest changes and take pride in their work. Over time, this approach leads to safer, more efficient, and more adaptable warehouse operations.
Warehouses that embrace continual process improvement achieve long-term success and stay ready for future challenges.
Regular warehouse audits play a crucial role in maintaining operational efficiency, accuracy, and compliance. These audits help teams identify inefficiencies, confirm quality standards, and support sustained productivity. Key benefits include cost reduction, improved safety, and higher customer satisfaction.
Expert consultants can offer valuable insights and help prioritize improvements for long-term success.
Next steps for organizations:
- Set clear audit objectives.
- Inventory all assets and review layout.
- Engage employees and analyze workflows.
- Implement changes and monitor progress.
- Schedule audits regularly and foster a culture of improvement.
FAQ
What is the ideal frequency for warehouse audits?
Most experts recommend quarterly audits. High-volume warehouses may benefit from monthly reviews. Regular audits help teams catch problems early and keep operations efficient.
Who should conduct a warehouse audit?
A trained internal team or an external consultant can lead the audit. Many companies use both for a balanced view. External auditors bring fresh perspectives and industry knowledge.
How does technology improve warehouse audits?
Technology like barcode scanners, RFID, and warehouse management systems speeds up data collection. These tools reduce errors and provide real-time insights. Teams can act on issues faster.
What are common issues found during audits?
Audits often reveal inventory discrepancies, safety hazards, and workflow bottlenecks. Teams may also find outdated equipment or missing training records. Addressing these issues boosts efficiency.
Why is staff involvement important in audits?
Employee input helps identify hidden problems. Staff members know daily challenges best. Their feedback leads to practical solutions and greater buy-in for changes.
Tip: Involve staff in every audit phase to build a culture of continuous improvement.
See Also
Essential Strategies To Improve Warehouse Inventory Movement
The Importance Of SaaS WMS In Modern Warehousing
How Intralogistics Advances Are Revolutionizing Warehouse Operations
Is Overflow Warehousing Key To Supporting E-commerce Expansion?
Three Methods Lean Logistics Enhances Supply Chain Sustainability